Influence of standardized evidence-based nursing practices on mental state and adverse effects in patients undergoing endoscopic colon polypectomy
- PMID: 40740894
- PMCID: PMC12305232
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.103736
Influence of standardized evidence-based nursing practices on mental state and adverse effects in patients undergoing endoscopic colon polypectomy
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic colon polypectomy is a common procedure used to remove polyps that may develop into colorectal cancer if left untreated. Despite these advantages, patients frequently experience anxiety and other adverse reactions. Standardized evidence-based nursing practices are essential for enhancing patient care by addressing both physical and psychological health issues.
Aim: To analyze the impact of standardized evidence-based nursing on psychological status and adverse reactions of patients undergoing endoscopic colonic polypectomy.
Methods: Data from 200 patients who underwent endoscopic colonic polypectomy at the authors' hospital between January and June 2024 were randomly assigned to two groups: Control [received routine nursing care (n = 100)] and study [received standardized evidence-based nursing intervention(s) (n = 100)]. Psychological status, visual analog scale, and Short-Form 36 Health Survey scores, adverse events, and satisfaction with nursing were compared between the two groups.
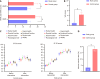
Results: After the interventions, the study group exhibited significantly lower scores on the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale and Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, along with a reduced incidence of adverse events compared with the control group (P < 0.05). Short-Form 36 Health Survey scores and overall satisfaction with nursing care were also significantly higher in the intervention group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Standardized evidence-based nursing interventions effectively reduced negative patient emotions and enhanced quality of life and satisfaction, demonstrating high safety.
Keywords: Adverse events; Colon polypectomy; Mental state; Nursing satisfaction; Standardized evidence-based nursing.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- He S, Xia C, Li H, Cao M, Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Teng Y, Li Q, Chen W. Cancer profiles in China and comparisons with the USA: a comprehensive analysis in the incidence, mortality, survival, staging, and attribution to risk factors. Sci China Life Sci. 2024;67:122–131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

