Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography features and pathological staging of gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps
- PMID: 40740919
- PMCID: PMC12305271
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.105136
Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography features and pathological staging of gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps
Abstract
Background: The diagnosis of gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps (IFPs) mainly depends on pathological confirmation after endoscopic or surgical treatment. Gastric IFP have typical manifestations under endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS), but atypical EUS features have also been reported. Previous studies have found that atypical features of gastric IFPs observed under EUS have corresponding histological manifestations. At present, there is no study elaborating the EUS manifestations of gastric IFPs at different pathological stages. We hypothesize that gastric IFPs at different pathological stages may have different EUS features.
Aim: To describe EUS features of gastric IFPs and compare with their pathological characteristics.
Methods: Clinical data of 53 inpatients with pathologically diagnosed gastric IFPs after endoscopic treatment were collected. All patients underwent preoperative EUS. We analyzed the EUS characteristics of the lesions and compared with the pathological characteristics and staging of the resected specimens.
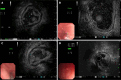
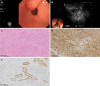
Results: Most gastric IFPs showed medium-low echo (67.9%), homogeneous echo (90.6%), and unclear boundaries (83%), and involved the second and third layers of the gastric wall (69.8%) under EUS. The echogenicity level and echo homogeneity were significantly correlated with the pathological stage of gastric IFP. Gastric IFPs in the nodular stage presented hypoechoic and homogeneous echo. Gastric IFPs in the fibrovascular stage mostly showed medium-low echo and homogeneous echo. Gastric IFPs in the sclerotic stage showed different echogenicity levels and echo homogeneity. The accuracy of EUS in diagnosing gastric IFPs was 66.0% (35/53), and the accuracy in determining the origin layer of gastric IFPs was 73.4% (39/53).
Conclusion: Gastric IFPs at different pathological stages have different EUS features. In order to improve the diagnostic rate, it is necessary to combine EUS with EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration or artificial intelligence.
Keywords: Endoscopic ultrasonography; Fibrovascular stage; Gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps; Nodular stage; Sclerotic stage.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kim YI, Kim WH. Inflammatory fibroid polyps of gastrointestinal tract. Evolution of histologic patterns. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988;89:721–727. - PubMed
-
- Matsushita M, Hajiro K, Okazaki K, Takakuwa H. Gastric inflammatory fibroid polyps: endoscopic ultrasonographic analysis in comparison with the histology. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;46:53–57. - PubMed
-
- Nagao S, Tsuji Y, Sakaguchi Y, Ushiku T, Koike K. Inflammatory fibroid polyp mimicking an early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92:217–218. - PubMed
-
- Garmpis N, Damaskos C, Garmpi A, Georgakopoulou VE, Sakellariou S, Liakea A, Schizas D, Diamantis E, Farmaki P, Voutyritsa E, Syllaios A, Patsouras A, Sypsa G, Agorogianni A, Stelianidi A, Antoniou EA, Kontzoglou K, Trakas N, Dimitroulis D. Inflammatory Fibroid Polyp of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Systematic Review for a Benign Tumor. In Vivo. 2021;35:81–93. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

