A state-of-the-art review of diffusion model applications for microscopic image and micro-alike image analysis
- PMID: 40740945
- PMCID: PMC12309395
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1551894
A state-of-the-art review of diffusion model applications for microscopic image and micro-alike image analysis
Abstract
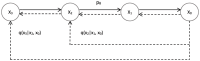
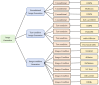
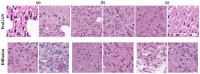
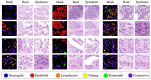
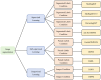
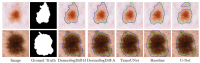
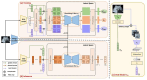
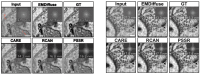
Diffusion models, a class of deep learning models based on probabilistic generative processes, progressively transform data into noise and then reconstruct the original data through an inverse process. Recently, diffusion models have gained attention in microscopic image analysis for their ability to process complex data, extract valuable information, and enhance image quality. This review provides an overview of diffusion models in microscopic images and micro-alike images, focusing on three commonly used models: DDPM, DDIM, and SDEs. We explore their applications in image generation, segmentation, denoising, classification, reconstruction and super-resolution. It shows their notable advantages, particularly in image generation and segmentation. Through simulating the imaging process of biological samples under the microscope, diffusion model can generate high-quality synthetic microscopic images. The generated images serve as a powerful tool for data augmentation when training deep learning models. Diffusion model also excels in microscopic image segmentation. It enables to accurately segment different cellular regions and tissue structures by simulating the interactions between pixels in an image. The review includes 31 papers, with 13 on image generation, nine on segmentation, and the remainder on other applications. We also discuss the strengths, limitations, and future directions for diffusion models in biomedical image processing.
Keywords: diffusion model; image analysis; image generation; image segmentation; micro-alike image; microscopic image.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Jiang, Li, Yuan, Grzegorzek, Li and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
A medical image classification method based on self-regularized adversarial learning.Med Phys. 2024 Nov;51(11):8232-8246. doi: 10.1002/mp.17320. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39078069
-
Influence of early through late fusion on pancreas segmentation from imperfectly registered multimodal magnetic resonance imaging.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2025 Mar;12(2):024008. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.12.2.024008. Epub 2025 Apr 26. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2025. PMID: 40291815
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Basavanhally A, Agner S, Alexe G, Bhanot G, Ganesan S, Madabhushi A. Manifold learning with graph-based features for identifying extent of lymphocytic infiltration from high grade, her2+ breast cancer histology. New York: Image Anal Appl Biol (in Conjunction MICCAI). (2008). Available online at: http://www.miaab.org/miaab-2008-papers/27-miaab-2008-paper-21.pdf (accessed March, 2024).
-
- Zettergren L, Nilsson F. Generation of synthetic white blood cell images using denoising diffusion (Master's Theses in Mathematical Sciences: ). Lund University (2023).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

