Nitidine chloride may mediate its antitumor effects by targeting kinesin family member 20A in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 40741189
- PMCID: PMC12305096
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i7.108666
Nitidine chloride may mediate its antitumor effects by targeting kinesin family member 20A in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of colorectal cancer (CRC) in younger people is increasing. Despite advances in precision medicine, the challenges of drug resistance and high costs persist. Nitidine chloride (NC) has pharmacological potential, and kinesin family member 20A (KIF20A) is overexpressed in various tumors; however, their interaction in CRC remains unexplored.
Aim: To investigate the KIF20A expression characteristics in CRC cells and determine whether it is a potential target gene for NC in inhibiting CRC treatment.
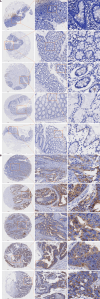
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), spatial transcriptomics, and mRNA expression profiling were used to analyze KIF20A expression in CRC cells. Immunohistochemical staining was used to verify KIF20A expression in 416 clinical samples (208 CRC tissue samples and 208 noncancerous control tissue samples). Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) technology was used to evaluate the impact of knocking out KIF20A on CRC cell growth. Molecular docking was applied to analyze NC-KIF20A binding. Finally, RNA sequencing and functional enrichment analysis were performed to explore the mechanism of action of NC in CRC cells.
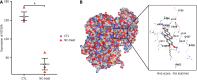
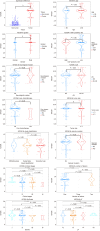
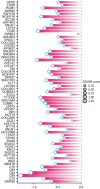
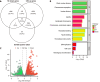
Results: Treating HCT116 cells with NC was found to significantly downregulate KIF20A (P < 0.05), and the molecular docking analysis revealed high-affinity binding between NC and KIF20A (binding energy = -9.6 kcal/mol). The scRNA-seq, spatial transcriptomics, and mRNA expression profiling results confirmed the significantly high expression of KIF20A in CRC tissues (standardized mean difference = 1.33, 95% confidence interval: 0.885-1.77, summary receiver operating characteristic curve area = 0.94). The immunohistochemical analysis of the clinical samples showed high KIF20A expression in the CRC tissues (P < 0.05), with significant correlation between the level of expression and gender, tumor size, and tumor grade (P < 0.05). Knocking out KIF20A significantly inhibited the growth of various CRC cell lines (CRISPR score < -0.3). The functional enrichment analysis indicated that NC may inhibit CRC by disrupting several biological processes, such as mitotic nuclear division, chromosome segregation, and microtubule binding.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that NC binds to KIF20A with high affinity and downregulates its expression in CRC cells, leading to reduced proliferation. Hence, NC has promise as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of CRC, and targeting KIF20A also has potential as a therapeutic strategy. Further KIF20A knockout studies are needed to confirm the binding specificity and mechanistic roles of NC in CRC.
Keywords: Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat screening; Colorectal cancer; Kinesin family member 20A; Molecular docking; Nitidine chloride; Single-cell sequencing.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Zheng Z, Wang L. Perspective on enhancing CRC risk prediction. Gut. 2025:gutjnl–2025. - PubMed
-
- Fang H, Dai W, Gu R, Zhang Y, Li J, Luo W, Tong S, Han L, Wang Y, Jiang C, Wang X, Wang R, Cai G. Correction: myCAF-derived Exosomal PWAR6 accelerates CRC liver metastasis via altering glutamine availability and NK cell function in the tumor microenvironment. J Hematol Oncol. 2025;18:31. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

