Pancreatic stone protein as a novel biomarker of microvascular complications in type II diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40741607
- PMCID: PMC12306870
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_211_24
Pancreatic stone protein as a novel biomarker of microvascular complications in type II diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Pancreatic stone protein (PSP) has been identified as an indicator of systemic stress and is elevated in individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), potentially serving as a prognostic marker for both the onset and progression of the disease.
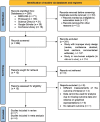
Materials and methods: This study was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis 2020 guidelines. Articles were sourced from MEDLINE, ProQuest, Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library electronic databases. Studies included are all observational studies examining PSP/Reg1α serum levels in patients with T2DM. The quality of the study was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale, as well as Review Manager 5.4 to perform the meta-analysis.
Results: Seven studies met the criteria for inclusion. Pooled analysis revealed significant differences in PSP values between T2DM individuals and healthy controls (standardized mean difference [SMD] = 2.14, 95% confidence interval CI: 1.05-1.92, P < 0.00001). Further subgroup analysis showed PSP was substantially higher in T2DM with complications (SMD = -1.57, 95% CI: -2.12 to -1.02, P < 0.00001) compared to T2DM without complications (SMD = -1.39, 95% CI: -2.17 to - 0.61) and newly diagnosed T2DM (SMD = -1.85, 95% CI: -2.96 to -0.74). Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations demonstrated moderate quality of evidence.
Conclusion: Our analysis revealed a progressive elevation in PSP values concomitant with the worsening T2DM disease state across the entire spectrum. PSP exhibits promising potential as a biomarker for predicting both disease initiation and subsequent clinical course.
Keywords: Pancreatic stone protein; Regenerating protein; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright: © 2025 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
