A GWAS Meta-meta-analysis and In-depth Silico Pharmacogenomic Investigations in Identification of APOE and Other Genes Associated with Pain, Anti-inflammatory, and Immunomodulating Agents in Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) Derived from 14.91 M Subjects
- PMID: 40742457
- PMCID: PMC12314298
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-025-01587-5
A GWAS Meta-meta-analysis and In-depth Silico Pharmacogenomic Investigations in Identification of APOE and Other Genes Associated with Pain, Anti-inflammatory, and Immunomodulating Agents in Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) Derived from 14.91 M Subjects
Abstract
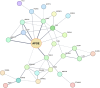
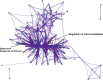
This study aimed to integrate genome-wide association studies (GWAS) with pharmacogenomics data to develop personalized pain and inflammatory therapeutics. Despite recent developments in the clinical utilities of pharmacogenomics, it needs more investigations for uncovering the complicated mechanisms of drugs from a genetic standpoint. The research addresses the increasing misuse of opioids during recovery, emphasizing personalized interventions for opioid use disorder (OUD). Key pain-related pathways were analyzed to uncover their interactions. Five GWAS traits, including pain, inflammatory biomarkers, immune system abnormalities, and opioid-related traits, were examined. Candidate genes extracted from GWAS datasets were refined through in silico analyses, including protein-protein interactions (PPIs), TF-miRNA coregulatory interactions, enrichment analysis (EA), and clustering enrichment analysis (CEA). A network of 50 highly connected genes was identified, with APOE emerging as a top candidate due to its role in cholesterol metabolism and opioid-induced lipid effects. Pharmacogenomics analysis highlighted significant gene annotations, including OPRM1, DRD2, APOE, GRIN2B, and GPR98, linking them to opioid dependence, neurological disorders, and lipid traits. Protein interaction analyses further validated these connections, with implications for epigenetic repair. Our findings reveal a strong association between APOE, opioid use, and Alzheimer's disease, suggesting potential for novel recovery strategies. Combining HDL-boosting drugs with pro-dopaminergic regulators like KB220 may help prevent relapse. This study underscores the importance of integrating genetic and pharmacogenomic data to advance personalized therapies.
Keywords: APOE; GWAS; Lipids; Meta-meta-analysis; Opioids; Pain.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Dr. Kenneth Blum reports royalties from and discloses many pending USA and foreign patents on GARS and KB220 variants licensed to Synaptamine and Victory Nutrition International. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work. Ethical Approval: Not applicable. Consent to Participate: Not applicable.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Precision medicine for mood disorders: objective assessment, risk prediction, pharmacogenomics, and repurposed drugs.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;26(7):2776-2804. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01061-w. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33828235 Free PMC article.
-
Does Preoperative Pharmacogenomic Testing of Patients Undergoing TKA Improve Postoperative Pain? A Randomized Trial.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Feb 1;482(2):291-300. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002767. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37594401 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pain management for women in labour: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Mar 14;2012(3):CD009234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009234.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22419342 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of GWAS identified SNPs associated with outcomes of medications for opioid use disorder.Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021 Nov 27;16(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13722-021-00278-y. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34838141 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association of lipid traits and lipid-related drug targets with normal tension glaucoma: a Mendelian randomization study for predictive preventive and personalized medicine.EPMA J. 2024 Jul 13;15(3):511-524. doi: 10.1007/s13167-024-00373-5. eCollection 2024 Sep. EPMA J. 2024. PMID: 39239107
References
-
- Anthony IC, Norrby KE, Dingwall T, Carnie FW, Millar T, Arango JC, Robertson R, Bell JE (2010) Predisposition to accelerated Alzheimer-related changes in the brains of human immunodeficiency virus negative opiate abusers. Brain 133(12):3685–3698 - PubMed
-
- Avila-Zozaya M, Zachariou V (2024) Genetic mouse models in opioid research: current status and future directions. J Neural Transm 131(5):491–494 - PubMed
-
- Blum K, Baron D (2019) Opioid substitution therapy: achieving harm reduction while searching for a prophylactic solution. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 20(3):180–182 - PubMed
-
- Blum K, Noble EP, Sheridan PJ, Montgomery A, Ritchie T, Jagadeeswaran P, Nogami H, Briggs AH, Cohn JB (1990) Allelic association of human dopamine D2 receptor gene in alcoholism. JAMA 263(15):2055–2060 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

