Practical Approaches to Patient-Centered Care in Europe: Mixed Methods Study Developing a Conceptual Framework for Comprehensive Cancer Care Networks
- PMID: 40743519
- PMCID: PMC12355145
- DOI: 10.2196/59683
Practical Approaches to Patient-Centered Care in Europe: Mixed Methods Study Developing a Conceptual Framework for Comprehensive Cancer Care Networks
Abstract
Background: In contemporary health care, patient-centered care has emerged as a pivotal paradigm shift that redefines the traditional physician-centric model. Particularly in the context of cancer care, marked by its intricate nature and emotional impact, there is a pressing requirement to rethink how health care is delivered. In this context, comprehensive cancer care networks (CCCNs) provide a new means of structuring and delivering quality cancer care, recognizing each patient's unique preferences and needs.
Objective: This study aimed to establish a consistent definition and framework for patient centeredness in CCCNs, facilitating the integration of a patient-centered approach to enhance care quality.
Methods: We conducted an umbrella review focusing on generic and oncology-specific dimensions of patient centeredness to establish the definition and framework. The data were analyzed and synthesized using an inductive category development approach, which guided the derivation of dimensions for the framework. The review was complemented by a survey of 23 key stakeholders within CCCNs and a focus group with patient representatives. This process involved iterative group discussions to achieve consensus on the framework and definition.
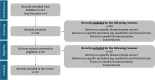
Results: The study presents a robust definition and framework of patient centeredness tailored to CCCNs, validated by an initial agreement rate of 96% among survey respondents. Patient centeredness in a CCCN is defined as a philosophy of care prioritizing the physical, emotional, and social needs and personal values of patients with cancer at every step of the patient pathway. In patient-centered CCCNs, patients are empowered and engaged in becoming active partners in health care in relation to their individual preferences and capabilities, with the goal of providing personalized, high-quality, holistic care with the best possible outcomes. The framework comprises 8 primary dimensions: empowering patients, engaging and involving patients, treating the patient as a unique person, enhancing the therapeutic relationship, enhancing a patient-centered culture, providing holistic care, recognizing and supporting the health care professional as a person, and coordinating care. Each dimension is supported by specific subdimensions and actionable patient-centered activities that facilitate practical implementation.
Conclusions: The results provide a comprehensive perspective on the complex elements that compose patient-centered care within CCCNs in Europe. This contributes to a better understanding and application of patient centeredness in cancer care and possibly other contexts. The results presented in this paper promise to support cancer care networks and other health care contexts in creating a patient-centered environment where patients feel genuinely heard, valued, and actively engaged in their care decisions.
Keywords: comprehensive cancer care networks; oncology; patient centeredness; patient empowerment; patient engagement.
©Emily Hickmann, Peggy Richter, Hannes Schlieter, Maja Cemazar, Dorota Dudek-Godeau, Nele Grapentin, Ellen Griesshammer, Marjetka Jelenc, Sigita Liutkauskiene, Alain Ravaud, Xavier Troussard, Simone Wesselmann. Originally published in JMIR Cancer (https://cancer.jmir.org), 31.07.2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures










References
-
- Bombard Y, Baker GR, Orlando E, Fancott C, Bhatia P, Casalino S, Onate K, Denis J, Pomey M. Engaging patients to improve quality of care: a systematic review. Implement Sci. 2018 Jul 26;13(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13012-018-0784-z. https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13012-... 10.1186/s13012-018-0784-z - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hickmann E, Richter P, Schlieter H. All together now - patient engagement, patient empowerment, and associated terms in personal healthcare. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Sep 02;22(1):1116. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08501-5. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-022-0... 10.1186/s12913-022-08501-5 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeSantis M, Hervas C, Weinman A, Bottarelli V. Patient empowerment. National Centre for Rare Diseases. [2025-05-29]. http://www.rd-action.eu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/PATIENT-EMPOWERMENT.pdf .
-
- Kuipers SJ, Cramm JM, Nieboer AP. The importance of patient-centered care and co-creation of care for satisfaction with care and physical and social well-being of patients with multi-morbidity in the primary care setting. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 Jan 08;19(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3818-y. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-018-3... 10.1186/s12913-018-3818-y - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sparidaens EM, Logger JG, Nelen WL, Braat DD, Fleischer K, Hermens RP. Web-based guidance for assisted reproductive technology with an online app (myFertiCare): quantitative evaluation with the HOT-fit framework. J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jan 24;25:e38535. doi: 10.2196/38535. https://www.jmir.org/2023//e38535/ v25i1e38535 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

