Dual-montage high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) modulates the neural dynamics serving working memory
- PMID: 40744248
- PMCID: PMC12426475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2025.121407
Dual-montage high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) modulates the neural dynamics serving working memory
Abstract
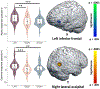
Verbal working memory (WM) is a critical cognitive construct supporting a broad range of daily functions. Neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of prefrontal-occipital circuitry in WM, but specific regional contributions and possible laterality effects remain unclear. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is an emerging technique that noninvasively modulates the excitability of neural populations, with studies showing stimulation effects on both local and distant but connected cortices. Herein, we utilized a novel dual-montage, high-definition tDCS (HD-tDCS) approach to evaluate the impact on functional brain dynamics and WM performance. Forty-five healthy adults underwent dual-montage HD-tDCS with 2.0 mA anodal stimulation applied over the midline occipital cortices and either the left or right dorsolateral prefrontal cortices (DLPFC) concurrently, or sham to both sites during three sessions. Following stimulation, participants completed a verbal WM task during magnetoencephalography (MEG). Whole-brain, voxel-wise maps were subjected to 1 × 3 repeated measure ANOVAs to probe stimulation effects. We found that left DLPFC-occipital stimulation induced stronger theta responses in the left superior temporal cortices, left supramarginal gyrus, left angular gyrus, and the right parietal cortices, while attenuated alpha responses were observed in the bilateral parietal cortices following right compared to left DLPFC-occipital stimulation and sham. Additionally, both active stimulation montages modulated oscillatory responses in the bilateral inferior frontal, the right lateral occipital cortices and other critical WM network regions during the encoding and maintenance phases. In conclusion, our results show that dual-montage anodal HD-tDCS differentially modulates spectrally and temporally distinct oscillatory responses, suggesting clear functional dissociations between left and right prefrontal regions during WM processing. These findings highlight the potential of tDCS in advancing our understanding of the unique contribution of each region in the network, which long-term could inform clinical interventions.
Keywords: Dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC); Dual-montage; Magnetoencephalography (MEG); Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS); Working memory (WM).
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors of this manuscript acknowledged no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures



References
-
- Achacheluee ST, Rahnama L, Karimi N, Abdollahi I, Arslan SA, Jaberzadeh S, 2018. The effect of unihemispheric concurrent dual-site transcranial direct current stimulation of primary motor and dorsolateral prefrontal cortices on motor function in patients with sub-acute stroke. Front. Hum. Neurosci 12, 441. 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arif Y, Embury CM, Spooner RK, Okelberry HJ, Willett MP, Eastman JA, Wilson TW, 2022. High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation of the occipital cortices induces polarity dependent effects within the brain regions serving attentional reorientation. Hum. Brain Mapp 43 (6), 1930–1940. 10.1002/hbm.25764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arif Y, Song RW, Springer SD, John JA, Embury CM, Killanin AD, Son JJ, Okelberry HJ, McDonald KM, Picci G, Wilson TW, 2024. High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation of the parietal cortices modulates the neural dynamics underlying verbal working memory. Hum. Brain Mapp 45 (12), e70001. 10.1002/hbm.70001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arif Y, Spooner RK, Wiesman AI, Proskovec AL, Rezich MT, Heinrichs-Graham E, Wilson TW, 2020. Prefrontal multielectrode transcranial direct current stimulation modulates performance and neural activity serving visuospatial processing. Cereb. Cortex 30 (9), 4847–4857. 10.1093/cercor/bhaa077. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

