Optimization of separation and purification processes in diethyl ether production for improved efficiency and sustainability
- PMID: 40744968
- PMCID: PMC12313844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10516-x
Optimization of separation and purification processes in diethyl ether production for improved efficiency and sustainability
Abstract
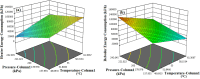
This study focuses on optimizing the separation and purification processes in diethyl ether (DEE) production to enhance energy efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality. Utilizing process simulation with Aspen-Hysys-V14, statistical modeling, and optimization techniques, this study investigates operational parameters across key units, including two drums and two distillation columns. Design of experiment was performed using response surface methodology (RSM) and central composite design (CCD). Key results indicate that under optimized conditions, a DEE purity of 96.43% was achieved with total energy consumption of 2,150,566 kJ/h, corresponding to an energy requirement of 1,499,754.87 kJ/kmol of DEE. Scenario-based optimization minimized DEE loss in fuel and vent streams while balancing energy demands. Non-linear relationships between parameters, such as temperature and pressure, were modeled with high predictive accuracy. These findings contribute to the development of sustainable and cost-effective DEE production processes and offer transferable insights for similar chemical manufacturing systems.
Keywords: Diethyl ether; Energy efficiency; Process optimization; Sustainability.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Performance and Emission Analysis of a Biogas-Diesel Dual-Fuel Engine Enhanced with Diethyl Ether Additives.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 8;10(28):30272-30294. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01509. eCollection 2025 Jul 22. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40727778 Free PMC article.
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Influence of Water Regeneration on Chemical and Process Indices in an Energy-Integrated PVC Production Process.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;17(12):1639. doi: 10.3390/polym17121639. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40574167 Free PMC article.
-
Wood Waste Valorization and Classification Approaches: A systematic review.Open Res Eur. 2025 May 6;5:5. doi: 10.12688/openreseurope.18862.2. eCollection 2025. Open Res Eur. 2025. PMID: 40438563 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Wu, L. et al. Process intensification of NaOH-catalyzed transesterification for biodiesel production by the use of bentonite and co-solvent (diethyl ether). Fuel186, 597–604 (2016).
-
- Encinar, J. M., Pardal, A. & Sánchez, N. An improvement to the transesterification process by the use of co-solvents to produce biodiesel. Fuel166, 51–58 (2016).
-
- Gargari, M. H. & Sadrameli, S. Investigating continuous biodiesel production from linseed oil in the presence of a Co-solvent and a heterogeneous based catalyst in a packed bed reactor. Energy148, 888–895 (2018).
-
- Kumar, M. V., Babu, A. V. & Kumar, P. R. The impacts on combustion, performance and emissions of biodiesel by using additives in direct injection diesel engine. Alexandria Eng. J.57, 509–516 (2018).
-
- Barik, D., Murugan, S., Samal, S. & Sivaram, N. Combined effect of compression ratio and diethyl ether (DEE) Port injection on performance and emission characteristics of a DI diesel engine fueled with upgraded biogas (UBG)-biodiesel dual fuel. Fuel209, 339–349 (2017).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

