Drug induced liver injury in HIV patients on dolutegravir based antiretroviral therapy regimens in Wolaita Sodo comprehensive specialized hospital
- PMID: 40744986
- PMCID: PMC12314119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13504-3
Drug induced liver injury in HIV patients on dolutegravir based antiretroviral therapy regimens in Wolaita Sodo comprehensive specialized hospital
Abstract
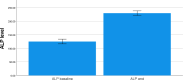
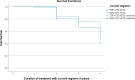
Drug induced liver injury is the most common and life-threatening condition associated with antiretroviral therapy. Dolutegravir (DTG) based combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) is currently first line treatment for HIV infected patients in Ethiopia. However, its effect on liver is not addressed. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the incidence of DTG based ART induced liver injury as first-line HIV treatment among peoples living with HIV. Hospital based retrospective cohort study was conducted in Wolaita Sodo Comprehensive Specialized Hospital ART unit, in South Ethiopia. Data was extracted from patient medical recording card. Non parametric Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the medians between groups for continuous variables and Fisher's exact test was employed for categorical variables. Univariate and multivariate survival Cox regression was employed to assess predictor variables for drug induced liver injury. The effect of the dolutegravir based regimen on liver enzymes were assessed with paired sample t-test. Kaplan Maier survival analysis was used to estimate mean survival function. A statistical significance was considered at p-value ≤ 0.05. Out of 234 patients on dolutegravir based combination therapy, 68 (29.1%) had drug induced liver injury (DILI). Predictors for DILI were higher baseline alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and experience with other ART. Among DILI cases, 67 (98.5) were associated with cholestatic type of drug induced liver injury. Only 1.5% had both cholestatic and hepatocellular type of DILI. There was significant increment in alanine aminotransferases (ALT), aspartate aminotransferases (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), body weight and blood glucose level (p < 0.001). However, there is no significant change in creatinine level (p > 0.05). The study demonstrated a significant elevation in liver enzymes, body weight and blood glucose levels in patients taking DTG based combination therapy. The most common drug induced liver injury was cholestatic type. Predictor variables for drug induced liver injury were increased baseline ALP and treatment history with other antiretroviral therapy.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; Dolutegravir; Drug induced liver injury; Human immunodeficiency virus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The data was collected for this research after approval from the Ethics Committee of Wolaita Sodo University of Science. The need for informed consent was waived by Wolaita Sodo University Institutional Review Board CHSM/ERC/06/16.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypertension among people living with HIV receiving dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23267. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06145-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603478 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous initiation of dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy and once-weekly rifapentine and isoniazid for tuberculosis prevention in antiretroviral-naive people with HIV: an open-label, non-randomised, phase 1/2 trial.Lancet HIV. 2025 Jun;12(6):e428-e439. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(25)00002-5. Epub 2025 May 8. Lancet HIV. 2025. PMID: 40349709 Clinical Trial.
-
Dolutegravir plus boosted darunavir versus recommended standard-of-care antiretroviral regimens in people with HIV-1 for whom recommended first-line non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor therapy has failed (D2EFT): an open-label, randomised, phase 3b/4 trial.Lancet HIV. 2024 Jul;11(7):e436-e448. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(24)00089-4. Epub 2024 May 21. Lancet HIV. 2024. PMID: 38788744 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) for treating HIV infection in ART-eligible pregnant women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;2010(3):CD008440. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008440. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20238370 Free PMC article.
-
Optimisation of antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected children under 3 years of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 22;2014(5):CD004772. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004772.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24852077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soriano, V. et al. Antiretroviral drugs and liver injury. AIDS22(1), 1–13 (2008). - PubMed
-
- <UNAIDS_GlobalplanCountryfactsheet_ethiopia_en.pdf>.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

