Disentangling extracellular current of electroactive bacteria with oblique-incidence reflection difference imaging
- PMID: 40745157
- PMCID: PMC12313974
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62467-6
Disentangling extracellular current of electroactive bacteria with oblique-incidence reflection difference imaging
Abstract
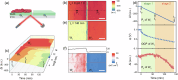
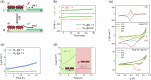
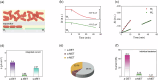
Understanding the extracellular electron transfer (EET) process of electroactive bacteria is of great significance. It is critical yet challenging to differentiate the partial currents from direct (DET) and mediated electron transfer (MET) pathways in the integrated EET current. Herein the EET current of model exoelectrogen is successfully disentangled by using spatiotemporally-resolved oblique-incidence reflection difference (OIRD) technique coupled with polyaniline (PANI)-based dual electrode. The PANI film serves as an electron acceptor to translate the charge information into OIRD signals, enabling mapping of EET current. Upon complete reduction of PANI, the local EET current is switched off, and the soluble mediators are forced to discharge on the nearby PANI electrode, enabling measuring of MET current. In such a way, the DET and MET currents are measured and the average currents from each bacterium are quantified. As-reported method enables successful disentangling the EET current and may offer valuable insights to related research.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Reguera, G. et al. Extracellular electron transfer via microbial nanowires. Nature435, 1098–1101 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Dong, F., Lee, Y. S., Gaffney, E. M., Liou, W. & Minteer, S. D. Engineering cyanobacterium with transmembrane electron transfer ability for bioelectrochemical nitrogen fixation. ACS Catal.11, 13169–13179 (2021).
-
- Zhang, Z. et al. Simultaneous reduction and methylation of nanoparticulate mercury: The critical role of extracellular electron transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol.58, 18368–18378 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Zang, Y. et al. Mechanism and applications of bidirectional extracellular electron transfer of Shewanella. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts25, 1863–1877 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

