The role of the ventral striatum in the relationship between impulsive decision-making and emotional self-regulation by cognitive reappraisal
- PMID: 40745372
- PMCID: PMC12313977
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13599-8
The role of the ventral striatum in the relationship between impulsive decision-making and emotional self-regulation by cognitive reappraisal
Abstract
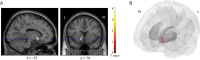
Delay discounting (DD), the preference for smaller, immediate rewards over larger, delayed ones, is a key measure of temporal impulsivity. While its link to behavioral self-regulation is well-studied, the relationship with emotional self-regulation is less understood. This study explored this relationship and its neuroanatomical mediators in the brain's reward system. We administered the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ) and a DD task to 155 young adult college students and collected structural MRI data. Our data revealed that greater use of cognitive reappraisal as an emotion regulation strategy was significantly associated with lower DD rates (i.e., reduced temporal impulsivity). No such relationship was found for expressive suppression. Furthermore, mediation analysis showed that higher cognitive reappraisal scores were associated with lower gray matter volume in the left ventral striatum, which in turn predicted lower DD. While the pattern of results is statistically consistent with full mediation, the cross-sectional nature of our data precludes causal inference. In conclusion, these results identify a novel neuroanatomical mechanism for temporal impulsivity. They suggest that cognitive reappraisal helps control impulsive choice and the process is mediated by the ventral striatum. This may provide a useful biomarker for developing interventions to improve self-control.
Keywords: Delay discounting; Emotion regulation; Intertemporal choice task; Reward system; Valuation; Ventral striatum.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Frost, R. & McNaughton, N. The neural basis of delay discounting: A review and preliminary model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.79, 48–65. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.04.022 (2017). https://doi.org/https://doi. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fields, S. A., Lange, K., Ramos, A., Thamotharan, S. & Rassu, F. The relationship between stress and delay discounting: a meta-analytic review. Behav. Pharmacol.25, 434–444 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Bechara, A. Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nat. Neurosci.8, 1458–1463 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

