Nationwide Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of 103 Patients With SH3TC2 Gene-Related Demyelinating Peripheral Neuropathy
- PMID: 40745932
- PMCID: PMC12313827
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.70313
Nationwide Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterisation of 103 Patients With SH3TC2 Gene-Related Demyelinating Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Autosomal recessive mutations in the SH3TC2 gene cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4C (CMT4C) demyelinating peripheral neuropathy.
Methods: In this nationwide observational retrospective study involving 27 French University Hospitals, we analyzed the clinical, electrophysiological, and genetic features of 103 patients from 89 families with homozygous and compound heterozygous SH3TC2 gene mutations identified between 2003 and 2023.
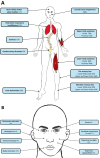
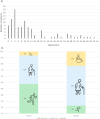
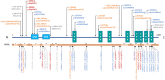
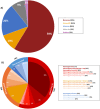
Results: Mean age was 42 years (2-80), and 49% of patients were female. Mean age at disease onset was 14 years (0-52), 60% of patients started the disease before age 10 years, and 24% after age 20 years. Patients presented with distal motor weakness (93% of cases), sensory loss (86%), foot deformities (83%), scoliosis (73%), proximal limb weakness (40%), cranial nerve involvement (48%), hearing loss (37%), scoliosis-related respiratory insufficiency (14%), and genitourinary disorders (6%). Half the patients (48%) walked independently before age 50 years, in contrast with only 13% after age 50 years. After age 50 years, 23% of patients were wheelchair-bound. Nerve conduction studies showed sensorimotor abnormalities within the demyelinating range in all cases. We identified 56 different pathogenic variants in the SH3TC2 gene, including 22 previously undescribed. Patients with two SH3TC2 gene truncating variants had more severe symptoms than patients with one or zero truncating variants.
Interpretation: This study shows CMT4C is a severe childhood- and adult-onset demyelinating peripheral neuropathy often associated with scoliosis, hearing loss, and ambulation loss in a significant proportion of patients after age 50 years. Genotype-phenotype correlations suggest two truncating SH3TC2 gene variants cause a more severe phenotype.
Keywords: CMT4C; Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease; SH3TC2 gene; SH3TC2 protein; Schwann cell; demyelinating polyneuropathy; myelin.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to report.
All the authors disclose conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SH3TC2-Related Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy.2008 Mar 31 [updated 2021 Mar 11]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2008 Mar 31 [updated 2021 Mar 11]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301514 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Charcot-Marie-Tooth-like presentation in giant axonal neuropathy: clinical variability and prevalence in a large Japanese case series.J Neurol. 2025 Jul 16;272(8):514. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13243-5. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40668264 Free PMC article.
-
The phenotype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C due to SH3TC2 mutations and possible predisposition to an inflammatory neuropathy.Neuromuscul Disord. 2009 Apr;19(4):264-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2009.01.006. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Neuromuscul Disord. 2009. PMID: 19272779
-
Screening for SH3TC2 gene mutations in a series of demyelinating recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT4).J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2016 Sep;21(3):142-9. doi: 10.1111/jns.12175. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2016. PMID: 27231023 Free PMC article.
-
Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an electrophysiological reappraisal and systematic review.J Neurol. 2017 Aug;264(8):1655-1677. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8474-3. Epub 2017 Mar 31. J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28364294
References
-
- Parmar J. M., Laing N. G., Kennerson M. L., and Ravenscroft G., “Genetics of Inherited Peripheral Neuropathies and the Next Frontier: Looking Backwards to Progress Forwards,” Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 95, no. 11 (2024): 992–1001, 10.1136/jnnp-2024-333436. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lousa M., Vázquez‐Huarte‐Mendicoa C., Gutiérrez A. J., Saavedra P., Navarro B., and Tugores A., “Genetic Epidemiology, Demographic, and Clinical Characteristics of Charcot‐Marie‐Tooth Disease in the Island of Gran Canaria (Spain),” Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System 24, no. 1 (2019): 131–138, 10.1111/jns.12299. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

