The role of epigenetics in pulmonary fibrosis: recent advances in mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 40746422
- PMCID: PMC12310491
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1647300
The role of epigenetics in pulmonary fibrosis: recent advances in mechanistic insights and therapeutic implications
Abstract
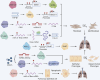
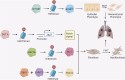
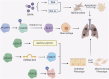
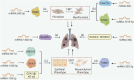
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a fatal disease characterized by progressive fibrosis of lung tissue, with a key pathological feature of excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix. PF occurs from complicated origins, while emerging findings have suggested the involvement of the environmental factors in the risk of PF through epigenetic regulation. This article will discuss how recent advances in epigenetic alterations of DNA methylation, RNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs contribute to PF development through molecular mechanisms and cellular processes, including fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition (FMT), epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), alveolar epithelial cell injury and immune cell interactions in the past 5 years.
Keywords: DNA methylation; RNA methylation; epigenetic regulation; histone modifications; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; non-coding RNA.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Qin, Zhu and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

