The insulator EACBE regulates V(D)J recombination of Tcrd gene by modulating chromatin organization
- PMID: 40746544
- PMCID: PMC12310595
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1613621
The insulator EACBE regulates V(D)J recombination of Tcrd gene by modulating chromatin organization
Abstract
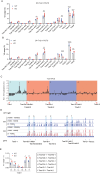
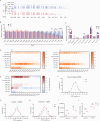
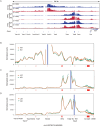
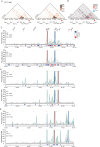
T cell receptor (TCR) diversity, essential for the recognition of a wide array of antigens, is generated through V(D)J recombination. The Tcra and Tcrd genes reside within a shared genomic locus, with Tcrd rearrangement occurring first in the double-negative (DN) stage during thymocyte development. Elucidating the regulatory mechanisms governing Tcrd rearrangement is therefore crucial for understanding the developmental coordination of both Tcrd and Tcra rearrangements. Chromatin architecture, orchestrated by CTCF-cohesin complexes and their binding sites, plays a fundamental role in regulating V(D)J recombination of antigen receptor genes. In this study, we report that EACBE, a CTCF binding element (CBE) located downstream of the Tcra-Tcrd locus, regulates Tcrd rearrangement. EACBE promotes the usage of proximal Vδ gene segments by facilitating spatial proximity between the Tcrd recombination centre and these Vδ elements. Notably, EACBE counteracts the insulating effects of INTs, two CBEs that demarcate the proximal V region from the Dδ-Jδ-Cδ cluster, thereby enabling effective chromatin extrusion. Furthermore, EACBE indirectly shapes the Tcra repertoire through its influence on Tcrd rearrangement. These findings reveal a novel regulatory axis involving special chromatin configuration and highlight distinct roles for specific CTCF binding sites in modulating antigen receptor gene assembly.
Keywords: CTCF binding element; T cell receptor; V(D)J recombination; chromatin activity; chromatin architecture.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Dai, Zhao, Luo, Li, Xue, Qin, Pan, Liao and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

