Association of the dietary index for gut microbiota and dietary inflammation index with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and metabolic alcohol-associated liver disease
- PMID: 40746546
- PMCID: PMC12310490
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593245
Association of the dietary index for gut microbiota and dietary inflammation index with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and metabolic alcohol-associated liver disease
Abstract
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and alcohol-associated metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease (MetALD) are significant public health concerns, with diet playing a pivotal role in their pathogenesis. Aims: Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007-2018. This study investigates the associations of the dietary index for gut microbiota (DI-GM), dietary inflammatory index (DII), and their combined effects with MASLD/MetALD, while exploring the mediating roles of inflammation and metabolic dysfunction.
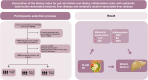
Methods: Data from the 2007 to 2018 NHANES included 9,529 participants. DI-GM and DII were calculated using 24-hour dietary recalls. Inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers-including triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index, metabolic score (MS), C-reactive protein (CRP), systemic immune inflammation index (SII), and systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI)-were analyzed. Multivariable logistic and linear regression, subgroup analyses, and restricted cubic spline (RCS) models assessed associations and dose-response relationships. Mediation analysis evaluated the roles of inflammatory and metabolic markers.
Results: Higher DI-GM scores were significantly associated with reduced MASLD (OR = 0.59, 95% CI: 0.46-0.75) and MetALD (OR = 0.57, 95% CI: 0.46-0.70). Conversely, higher DII scores were positively associated with MASLD (OR = 1.57, 95% CI: 1.23-2.01) and MetALD (OR = 1.40, 95% CI: 1.13-1.75). DI-GM was inversely associated with inflammation and metabolic markers (TyG: β= -0.05, MS: β= -0.11, CRP: β= -0.12, SII: β= -0.08, SIRI: β= -0.09), while DII exacerbated these markers (TyG: β= 0.06, MS: β= 0.18, CRP: β=0.14, SII: β= 0.11, SIRI: β= 0.10). The combined effects of DI-GM and DII further demonstrated that a gut microbiota-healthy and anti-inflammatory diet synergistically reduced MASLD (OR = 0.59, 95% CI: 0.43-0.81) and MetALD risks (OR = 0.58, 95% CI: 0.44-0.76). Mediation analysis confirmed that inflammation and metabolism significantly mediated the diet-disease associations (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Higher DI-GM and lower DII are associated with reduced MASLD/MetALD risks, partially mediated by alleviating systemic inflammation and metabolic dysfunction. These findings highlight dietary interventions targeting gut microbiota and inflammation as strategies for early prevention of MASLD and MetALD.
Keywords: alcohol-associated metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease; dietary index for gut microbiota; dietary inflammatory index; inflammation; metabolic dysfunction; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Copyright © 2025 Wu and Hou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. (2015) 148:547–55. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.039, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

