"Molecular pigeon" network of lncRNA and miRNA: decoding metabolic reprogramming in patients with lung cancer
- PMID: 40746614
- PMCID: PMC12310638
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1578927
"Molecular pigeon" network of lncRNA and miRNA: decoding metabolic reprogramming in patients with lung cancer
Abstract
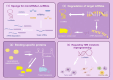
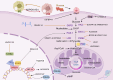
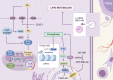
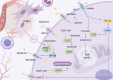
In recent years, with the advancement of RNA analysis techniques, such as single-cell RNA sequencing, noncoding RNAs have demonstrated substantial potential in regulating gene expression, encoding peptides and proteins, constructing the cellular microenvironment, and modulating cell function. They can serve as potential therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for various diseases, offering novel avenues for diagnosis and treatment. Among them, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent a principal component. Through the competing endogenous RNA mechanism, lncRNAs sequester microRNAs (miRNAs), interact with metabolic enzymes or transcription factors, regulate gene expression, and participate in the metabolic communication network within the tumor microenvironment. This process significantly promotes the growth, proliferation, and metastasis of lung cancer cells by reprogramming core metabolic pathways-including glucose utilization, lipid homeostasis, and amino acid flux. This article reviews the key roles of lncRNAs and miRNAs in the metabolic reprogramming of patients with lung cancer, elucidates the complex lncRNA-miRNA network involved, and provides mechanistic insights into metabolic vulnerabilities and translational opportunities for targeted interventions in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: NSCLC; lncRNA; lung cancer; metabolic reprogramming; miRNA.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Dai, Chen, Deng, Wang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis of prognostic-related lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs forming a competing endogenous RNA network in lung squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Jul;146(7):1711-1723. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03224-8. Epub 2020 Apr 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32356177 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the role of novel long noncoding RNAs lnc-SLC6A12-1:3 and lnc-SLC6A12-7:5 in regulating the expression of GAD1 and SLC6A12 in cholangiocarcinoma.Comput Biol Chem. 2025 Jun 20;119:108562. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2025.108562. Online ahead of print. Comput Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40578094
-
Multidimensional communication of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Jan;145(1):31-48. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2767-5. Epub 2018 Nov 11. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30417217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural products and long non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer: insights into etiology and treatment resistance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6349-6368. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03736-x. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39825964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of Concern.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2025 Jun;29(6):287-288. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202506_37270. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40613620
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

