Regorafenib Induced Interstitial Pneumonia in a Patient With Refractory Rectal Cancer
- PMID: 40746636
- PMCID: PMC12308151
- DOI: 10.1002/rcr2.70286
Regorafenib Induced Interstitial Pneumonia in a Patient With Refractory Rectal Cancer
Abstract
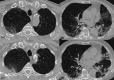
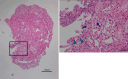
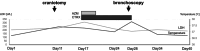
Regorafenib, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), is indicated for refractory colorectal carcinoma, gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We present a case involving a 66-year-old male patient with refractory colorectal cancer who developed interstitial pneumonia as a consequence of regorafenib therapy. Three months following the initiation of regorafenib administration, a chest computed tomography scan revealed bilateral ground-glass opacities, a characteristic finding in interstitial lung disease. This case illustrates a relatively rapid progression of regorafenib-induced interstitial lung disease following its radiographic manifestation. Clinicians should remain vigilant for this potential pulmonary toxicity in patients receiving regorafenib, even with an apparently short latency period after treatment commencement. Early recognition and prompt intervention are crucial in managing this adverse event.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; drug‐induced interstitial lung disease; interstitial pneumonia; multi‐targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor; regorafenib.
© 2025 The Author(s). Respirology Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wilhelm S. M., Dumas J., Adnane L., et al., “Regorafenib (BAY73‐4506): A New Oral Multikinase Inhibitor of Angiogenic, Stromal and Oncogenic Receptor Tyrosine Kinases With Potent Preclinical Antitumor Activity,” International Journal of Cancer 129 (2011): 245–255. - PubMed
-
- Grothey A., Van Cutsem E., Sobrero A., et al., “Regorafenib Monotherapy for Previously Treated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CORRECT): An International, Multicentre, Randomised, Placebo Controlled, Phase 3 Trial,” Lancet 381 (2013): 303–312. - PubMed
-
- Demetri G. D., Reichardt P., Kang Y. K., et al., “Efficacy and Safety of Regorafenib for Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumours After Failure of Imatinib and Sunitinib (GRID): An International, Multicentre, Randomised, Placebo‐Controlled, Phase 3 Trial,” Lancet 381 (2013): 295–302. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruix J., Qin S., Merle P., et al., “Regorafenib for Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Progressed on Sorafenib Treatment (RESORCE): A Randomised, Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled, Phase 3 Trial,” Lancet 389 (2017): 56–66. - PubMed
-
- Bayer , Guide to Proper Use of Regorafenib for HCC/Colorectal Cancer/GIST, 2025, https://pharma‐navi.bayer.jp/stivarga/usage‐safety/postmarket‐safety‐inf....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

