Exogenous Spatial Attention Helps Overcome Spatial Specificity of Visual Learning in the Blind Field After V1 Damage
- PMID: 40746664
- PMCID: PMC12312055
- DOI: 10.1007/s41465-024-00307-z
Exogenous Spatial Attention Helps Overcome Spatial Specificity of Visual Learning in the Blind Field After V1 Damage
Abstract
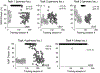
Visual discrimination training can restore visual functions in the blind field of participants with stroke-induced V1 damage. However, single-stimulus training in this population is limited by spatial specificity. Thus, it requires iterative training over several months to achieve improvement at more than one blind-field location, particularly at sites further from the blind field border (i.e., deeper in the blind field). With neurotypical observers, exogenous spatial attention (SA) facilitates transfer of learning to untrained locations. Here, we asked if SA pre-cues could induce transfer of training deeper into cortically blinded (CB) fields. Twenty CB participants trained on a global motion discrimination task either using a single [primary] stimulus and no cues (Task 1), a single primary stimulus with a large pre-cue deep in the blind field (Task 2), two identical stimuli (primary and deep) with small pre-cues just above them (Task 3), or a single stimulus randomly alternating at a primary and deep blind-field location, forewarned by a small pre-cue above them on each trial (Task 4). Training on Task 1 induced reliable improvements at the primary location, but no transfer of learning deeper in the blind field. The addition of SA pre-cues in Tasks 2-4 induced transfer in more than half the participants, although threshold improvements at primary locations were smaller than for Task 1. We conclude that directing exogenous SA deep in the blind field attracts attention automatically in CB patients and facilitates transfer of learning towards cued locations, even without V1 processing for those regions of space.
Keywords: Hemianopia; Motion perception; Perceptual learning; Stroke; Transfer; Vision restoration.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Krystel R. Huxlin is an editor at Journal of Cognitive Enhancement and is an inventor on US Patent No. 7,549,743. All others: none.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
