Efficacy of image-guided accurate limbal relaxing incisions for astigmatism correction during cataract surgery
- PMID: 40746871
- PMCID: PMC12310401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aopr.2025.06.001
Efficacy of image-guided accurate limbal relaxing incisions for astigmatism correction during cataract surgery
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the efficacy of image-guided accurate limbal relaxing incisions (LRIs) for astigmatism correction during cataract surgery.
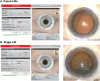
Methods: Consecutive cataract patients with regular corneal astigmatism ranging from 0.75 to 2.50 D, intended for cataract surgery with image-guided LRIs, were recruited in this prospective cohort study. The efficacy of astigmatism correction was evaluated 3 months after surgery, and compared among eyes with preoperative corneal with-the-rule (WTR), against-the-rule (ATR) and oblique astigmatism. Higher-order aberrations and visual quality indices obtained with iTrace were further compared between eyes with single and paired LRIs.
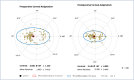
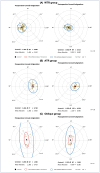
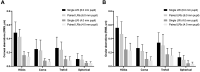
Results: Totally, 108 eyes of 108 patients were analyzed. The mean total surgical induced astigmatism (tSIA) vector of all participants was 0.76 ± 0.38 D (range: 0.11-1.79 D, preoperative vs. postoperative astigmatism: 1.46 ± 0.41 vs. 0.78 ± 0.44 D, P < 0.001). Eyes with WTR astigmatism showed higher tSIA (0.89 ± 0.32 D vs. 0.42 ± 0.21 D vs. 0.48 ± 0.36 D, respectively, P < 0.001), as well as higher correction index and lower difference vector and index of success than ATR and oblique astigmatism groups (all P < 0.05). Eyes with paired LRIs exhibited better corneal average height of modulation transfer function, a better corneal performance index and a better quality of vision index than those with single LRI (all P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Image-guided LRIs can effectively correct low-to-moderate corneal astigmatism during cataract surgery, especially in eyes with WTR astigmatism.
Keywords: Astigmatism correction; Cataract surgery; Image-guided accurate limbal relaxing incisions; Visual quality.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Surgical Methods for the Correction of Low Amounts of Corneal Astigmatism during Cataract Surgery.Ophthalmology. 2025 Jun 16:S0161-6420(25)00360-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2025.06.011. Online ahead of print. Ophthalmology. 2025. PMID: 40532854
-
Different-sized incisions for phacoemulsification in age-related cataract.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 20;9(9):CD010510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28931202 Free PMC article.
-
Manual versus femtosecond laser-assisted relaxing incisions for correction of low astigmatism in implantable collamer lens surgery.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 1;73(7):980-987. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2012_24. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40586187 Free PMC article.
-
Topography-guided subconjunctival oblique limbus incisions (SCOLI) in manual cataract surgery for astigmatism correction.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 18. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2532_24. Online ahead of print. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40679422
-
Excimer laser refractive surgery versus phakic intraocular lenses for the correction of moderate to high myopia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 17;2014(6):CD007679. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007679.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24937100 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

