Potential of edible insects as alternative protein source for the older adults
- PMID: 40747292
- PMCID: PMC12311957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101153
Potential of edible insects as alternative protein source for the older adults
Abstract
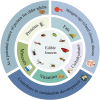
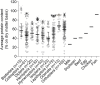
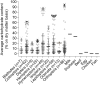
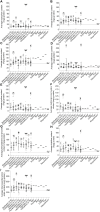
With global population growth and aging, the demand for high-quality protein continues to increase. It is therefore important to find new and sustainable sources of protein. Compared to traditional animal-derived proteins, insect-derived proteins have higher sustainability and a smaller ecological footprint. In addition, considering that older adults have an anabolic resistance and that protein intake strongly stimulates skeletal muscle protein synthesis, insect-derived proteins may play a potential role in promoting healthy aging. Based on this, this review systematically analyzes the essential amino acid profile, nutritional value, protein digestibility and absorption, health benefits and potential risks, as well as the acceptability and environmental impact of edible insects. Overall, adding insect-derived protein to the diet helps maintain skeletal muscle mass and function in aging, improves gut health, and lowers the risk of age-related diseases. In future research, it is still necessary to improve processing and preparation techniques and establish explicit legal provisions to ensure the safety and acceptability of insect-derived proteins.
Keywords: Amino acids profile; Health benefits; Healthy aging; Insect-derived proteins; Potential risks.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Ademolu K.O., Simbiat E.S., Concilia I.I., et al. Gender variations in nutritive value of adult variegated grasshopper , Zonocerus variegatus (L) (Orthoptera:Pygomorphidae), J. Kansas. Entomol. Soc. 2017;90:117–121. doi: 10.2317/170325.1. - DOI
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

