Decreased Serum Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Level Is Associated With Renal Function Impairment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 40747293
- PMCID: PMC12313390
- DOI: 10.1155/jdr/9987648
Decreased Serum Adipose Triglyceride Lipase Level Is Associated With Renal Function Impairment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
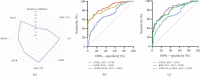
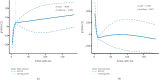
Background: Diagnosing diabetic kidney disease (DKD) remains a significant challenge. Research has increasingly focused on kidney injury resulting from lipid metabolism disorders. Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), a pivotal enzyme in lipolysis, is essential for maintaining lipid metabolism balance. The objective of this study was to assess whether serum ATGL could serve as an early biomarker for DKD. Methods: The study divided 236 participants into four groups: healthy controls (n = 59), Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) < 30 mg/g (n = 80), microalbuminuria (L-DKD) with ACR 30-300 mg/g (n = 41), and macroalbuminuria (H-DKD) with ACR ≥ 300 mg/g (n = 56). Relevant clinical data were collected, and serum levels of ATGL, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and tumor necrosis factor-1 (TNFR-1) were measured. Various statistical analyses, including Spearman's correlation test, receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, multivariate logistic regression, and restricted cubic spline (RCS), were employed to assess the relationship between serum ATGL levels and renal function impairment in DKD. Results: Serum ATGL levels were notably lower in the T2DM, L-DKD, and H-DKD groups compared to healthy controls. Positive correlations were found between serum ATGL levels and estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR), while negative correlations were observed with diabetes duration, hypertension history, hyperlipidemia, urine ACR (UACR), 24-h urine total protein (UTP), serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen, uric acid, TNFR-1, and KIM-1/creatinine (KIM-1/Cr) levels (p < 0.05). The receiver operating characteristic curve analysis demonstrated that the diagnostic performance of ATGL, when combined with traditional clinical markers, can enhance sensitivity. When participants were grouped by serum ATGL quartiles, it was observed that higher ATGL levels corresponded with lower UACR, 24 h-UTP, SCr, and TNFR-1 levels and higher eGFR. The odds ratios for elevated UACR and 24 h-UTP decreased, and eGFR increased with higher ATGL quartiles. Both univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses indicated that serum ATGL is a protective factor against DKD development, even after adjusting for potential confounders. RCS analysis indicated a nonlinear dose-response association between serum ATGL levels and renal function metrics, specifically UACR and eGFR, in patients with DKD. Conclusion: Serum ATGL levels are linked to reduced renal function in T2DM patients. A decline in ATGL levels corresponded with a nonlinear rise in UACR and a drop in eGFR, suggesting that serum ATGL may serve as a potential biomarker for DKD development.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; biomarker; diabetic kidney disease; serum ATGL.
Copyright © 2025 Ying Wang et al. Journal of Diabetes Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Foreman K. J., Marquez N., Dolgert A., et al. Forecasting Life Expectancy, Years of Life Lost, and All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality for 250 Causes of Death: Reference and Alternative Scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 Countries and Territories. Lancet . 2018;392(10159):2052–2090. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31694-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

