Metformin carbon dots-based osteogenic and protein delivery system to promote bone regeneration in periodontitis
- PMID: 40747455
- PMCID: PMC12312117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.07.001
Metformin carbon dots-based osteogenic and protein delivery system to promote bone regeneration in periodontitis
Abstract
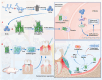
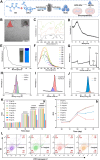
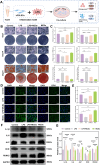
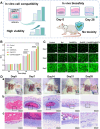
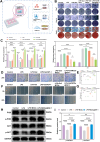
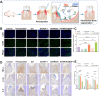
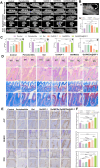
The chronic inflammation in periodontitis suppresses the osteogenic potential of human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs), posing a significant challenge to endogenous bone regeneration. To address this, we developed an osteogenic and protein-delivery composite hydrogel system based on metformin carbon dots (MCDs) to enhance the osteogenic potential of hPDLSCs under inflammatory conditions. We successfully synthesized a novel Gel/MCDs@IGF-1 composite hydrogel (Gel) that exhibited excellent biocompatibility and sequentially released MCDs and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). First, MCDs were synthesized using a one-step hydrothermal method. MCDs promote the osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs under lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory conditions by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and alleviate inflammation. Next, MCDs and IGF-1 were assembled into MCDs@IGF-1 complexes through supramolecular interactions, facilitating efficient IGF-1 delivery and reducing its degradation by trypsin. Furthermore, in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that the Gel/MCDs@IGF-1 composite hydrogel effectively recruited stem cells, exerted early anti-inflammatory effects, increased the osteogenesis of hPDLSCs under inflammatory conditions, and significantly promoted alveolar bone regeneration in a Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat model of periodontitis. In conclusion, MCDs, with their dual roles in promoting osteogenesis and protein delivery, are a promising candidate nanoplatform for periodontitis therapy. Additionally, the MCDs-based sequential release hydrogel system presents a novel material strategy for the treatment of periodontitis.
Keywords: Carbon dots; IGF-1; Metformin; Osteogenic differentiation; Protein delivery.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Đorđević I.O., Kukolj T., Krstić J., Trivanović D., Obradović H., Santibañez J.F., Mojsilović S., Ilić V., Bugarski D., Jauković A. The inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells osteogenic differentiation by IL-17 is mediated via MAPKs. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016;71:92–101. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.12.007. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

