Risk Factor of Blastocystis hominis and Giardia duodenalis among Stunted Children in Bandung Regency, Indonesia
- PMID: 40747504
- PMCID: PMC12307786
- DOI: 10.18502/ijpa.v20i2.19048
Risk Factor of Blastocystis hominis and Giardia duodenalis among Stunted Children in Bandung Regency, Indonesia
Abstract
Background: Stunting, resulting from chronic malnutrition, increases susceptibility to infections due to immature immunity. Blastocystis hominis and Giardia duodenalis may contribute to stunting. We aimed to determine the characteristics of intestinal protozoan infection among stunting children.
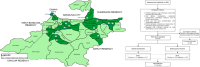
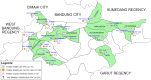
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 2020 among 280 stunted children in Bandung Regency, West Java, Indonesia. Faecal specimens were collected, with portions preserved separately in 10% formaldehyde and RNA Later solution. Of these, 230 met the examination criteria. Risk factors and demographic data were obtained through interviews. DNA was extracted, and intestinal protozoan infection were detected using PCR targeting the 18S SSU rRNA gene for B. hominis and 16S-like RNA gene for G. duodenalis.
Results: The prevalence of G. duodenalis and B. hominis was 5.6% (13/230) and 55.6% (128/230), respectively. Multivariate analysis identified age (P-value 0.004; OR 0.327) and no availability of a septic tank (P-value 0.021; OR 4.881) were the significant risk factors for G. duodenalis infection. For B. hominis infection, significant risk factors included age (P-value 0.033; OR 0.722) and gender (P-value 0.047; OR 1.742).
Conclusion: Stunting and intestinal protozoan infection present a dual burden. G. duodenalis and B. hominis infections were prevalent among stunted children. Significant risk factors included age and septic tank unavailability for G. duodenalis, while age and gender were associated with B. hominis infection. Improved sanitation and targeted interventions are essential to reduce infection risks.
Keywords: Blastocystis hominis; Children; Giardia duodenalis; Intestinal protozoan infection; Stunting.
© 2025 Fauziah et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wong LW, Ong KS, Khoo JR, et al. Human Intestinal Parasitic Infection: A Narrative Review on Global Prevalence and Epidemiological Insights on Preventive, Therapeutic and Diagnostic Strategies for Future Perspectives. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;14(11):1093–1105. - PubMed
-
- Maryanti E, Lesmana SD, Mandela H. Deteksi Protozoa Usus Oportunistik pada Penderita Diare Anak di Puskesmas Rawat Inap Pekanbaru. Jurnal Ilmu Kedokteran. 2017;9(1):22–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
