Phage-displayed synthetic library and screening platform for nanobody discovery
- PMID: 40748049
- PMCID: PMC12316454
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.105887
Phage-displayed synthetic library and screening platform for nanobody discovery
Abstract
Nanobodies, single-domain antibodies derived from camelid heavy-chain antibodies, are known for their high affinity, stability, and small size, which make them useful in biological research and therapeutic applications. However, traditional nanobody generation methods rely on camelid immunization, which can be costly and time-consuming, restricting their practical feasibility. In this study, we present a phage-displayed synthetic library for nanobody discovery. To validate this approach, we screened nanobodies targeting various Drosophila secreted proteins. The nanobodies identified were suitable for applications such as immunostaining and immunoblotting, supporting the phage-displayed synthetic library as a versatile platform for nanobody development. To address the challenge of limited accessibility to high-quality synthetic libraries, this library is openly available for non-profit use.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; biochemistry; chemical biology; nanobody screen; phage-display; secreted protein; synthetic library.
© 2025, Xia, Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
BX, AK, FL, MH, ES, SM, FD, SM, AR, NP No competing interests declared
Figures

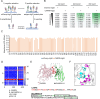
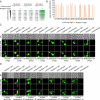
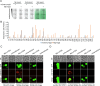
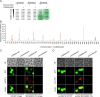

Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.12.20.629765
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.105887.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.105887.2
References
-
- Evans R, Pritzel A, Antropova N, Senior A, Green T, Bates R, Blackwell S, Jain R, Clancy E, Jumper J, Yim J. Protein complex prediction with alphafold-multimer. bioRxiv. 2022 doi: 10.1101/2021.10.04.463034. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

