Clear Native Gel Electrophoresis for the Purification of Fluorescently Labeled Membrane Proteins in Native Nanodiscs
- PMID: 40748368
- PMCID: PMC12355471
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01702
Clear Native Gel Electrophoresis for the Purification of Fluorescently Labeled Membrane Proteins in Native Nanodiscs
Abstract
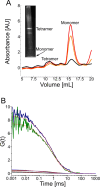
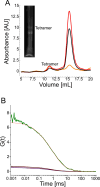
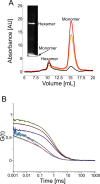
Native gel electrophoresis techniques, such as blue or clear native gel electrophoresis (BNE or CNE), are widely used to separate and characterize proteins. However, in high-resolution CNE, mild anionic or neutral detergents are often used at concentrations that are too low to prevent membrane-protein aggregation. Additionally, the identification of proteins is hampered by the lack of suitable molecular-weight markers such as those used in SDS-PAGE. Here, we introduce a novel approach that combines charged polymer-encapsulated nanodiscs and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) to address both challenges. Membrane proteins are first extracted using Glyco-DIBMA, a negatively charged amphiphilic copolymer. This enables the spontaneous formation of nanodiscs harboring the fluorescently labeled target protein within a native-like lipid-bilayer environment, which is confirmed by FCS. The nanodiscs are then subjected to detergent-free CNE. As the number of protomers increases, the nanodiscs grow larger, resulting in increased migration distances in CNE due to higher charge densities. Crucially, the nanodiscs remain intact throughout the CNE, as demonstrated by FCS analysis of resolubilized bands excised from the gels. Moreover, the membrane proteins used in this study, a potassium channel (KvAP), a sodium channel (NavMs), a water channel (GlpF), and a urea channel (HpUreI), show only negligible aggregation, as evidenced by the fluorescent brightnesses and diffusion times of individual nanodiscs. In addition, the oligomeric states of membrane proteins can be deduced from the brightness per nanodisc. Since purified membrane proteins remain within a native-like lipid-bilayer environment and avoid detergent exposure, they are immediately suitable for downstream structural and functional studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Electrophoresis.2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36251838 Free Books & Documents.
-
Home is where the lipids are: a comparison of MSP and DDDG nanodiscs for membrane protein research.Soft Matter. 2025 Aug 20;21(33):6596-6602. doi: 10.1039/d5sm00327j. Soft Matter. 2025. PMID: 40762966
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Topical antiseptics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013055. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013055.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484403
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

