Relationships between nitrogen-fixing bacteria community structure in Vicia villosa nodules, soil properties and rocky desertification degree in karst area southwest China
- PMID: 40748871
- PMCID: PMC12316310
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329408
Relationships between nitrogen-fixing bacteria community structure in Vicia villosa nodules, soil properties and rocky desertification degree in karst area southwest China
Abstract
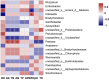
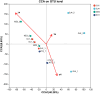
Rocky desertification, a common phenomenon in karst ecosystems, significantly impacts soil fertility and vegetation restoration. Therefore, understanding the relationship between nitrogen-fixing bacteria and soil properties under different degrees of rocky desertification is crucial. Our experiment was conducted to investigate the bacterial community structure and the main environmental factors affecting the distribution of the nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nodules of V. villosa. Based on nifH gene sequence analysis, we found that the community composition of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nodules was significantly correlated with the degree of rocky desertification. The soil physicochemical properties affecting community composition were analyzed. The results revealed that: (1) The soil water content, alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen content, and total nitrogen content in the slight rocky desertification area GJ4 were significantly higher than those in the moderate rocky desertification areas KY and MZ3. (2) There were significant differences in the community composition of nitrogen-fixing bacteria across the four rocky desertification areas (R2 = 0.448, P = 0.001). Within the same area, the Shannon index in slight rocky desertification was significantly higher than that of moderate rocky desertification. Rhizobium was the dominant genus. (3) In Gejiu, Yunnan Province, it has been observed that there is a clear negative correlation was observed among rocky desertification grade, soil water content, and nitrogen-fixing bacterial diversity in the typical karst ecosystem. Specifically, intensifying rocky desertification significantly reduces soil moisture and bacterial diversity. The degree of soil rocky desertification, total nitrogen content, total phosphorus content, and pH of soil are the main factors that play a key role in the community composition of the nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nodules of V. villosa. This study provides a theoretical basis for the control of rocky desertification.
Copyright: © 2025 Qi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Wang S, Li Y, Li R. Karst rocky desertification: formation background, evolution and comprehensive taming. Quaternary Sciences. 2003;(06):657–66.
-
- Liu F, Wang S, Liu Y, He T, Luo H, Long J. Changes of soil quality in the process of karst rocky desertification and evaluation of impact on ecological environment. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 2005;(03):639–44.
-
- Qin X, Zhu M, Jiang Z. A review on recent advances in rocky desertification in southwest China karst region. Carsologica Sinica. 2006;(03):234–8.
-
- Gu Y, Chen F, Li K, Wu H. Ecological control of land rocky desertification and vegetation recovery in karst region of Yunnan Province. Sci Technol Review. 2009;27(05):75–80.
-
- Liu L, He X, Du H, Wang K. The relationships among nitrogen-fixing microbial communities, plant communities, and soil properties in karst regions. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 2017;37(12):4037–44.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

