Biochemical neuroplasticity in the cerebellum after physical exercise: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40748906
- PMCID: PMC12316286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309259
Biochemical neuroplasticity in the cerebellum after physical exercise: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
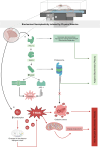
Background: Neuroplasticity is the central nervous system's (CNS) capacity to adapt to injuries or environmental changes. Biochemical neuroplasticity is one such adaptation that may occur in response to physical exercise (PE). This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effects of PE on cerebellar biochemical neuroplasticity.
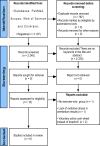
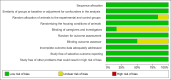
Methods: Following the PICO strategy, this review included in vivo studies with small rodents (Population) subjected to well-defined PE protocols (Intervention) and compared to non-exercised controls (Comparator) to assess cerebellar biochemical alterations (Outcome). Studies published between January 1976 and July 2024 without language restrictions were searched in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central databases. Data were synthesized through meta-analyses and methodological quality was assessed by the SYRCLE risk of bias tool.
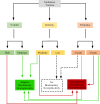
Results: Out of 3,107 records screened, six studies met the inclusion criteria for qualitative and quantitative analyses. All studies had a low or unclear risk of bias. Markers of biochemical neuroplasticity assessed included superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione (GR), reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), glutathione disulphide (GSSG) and lipid peroxidation (LPO). Meta-analyses showed that moderate-volume PE significantly reduced LPO (SMD = -2.41; 95% CI: -3.89 to -0.93), while high-volume PE increased LPO (SMD = 4.55; 95% CI: 1.92 to 7.18). Low-intensity or low-volume PE did not significantly alter oxidative markers.
Conclusions: PE induces either adaptive or maladaptive biochemical neuroplasticity in the cerebellum depending on protocol variables. While enzymatic activity responds to cellular changes and limits nervous tissue protection, adaptive biochemical neuroplasticity seems to confer greater resistance and efficiency.
Copyright: © 2025 Corrêa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Deppermann S, Storchak H, Fallgatter AJ, Ehlis AC. Stress-induced neuroplasticity: (Mal)adaptation to adverse life events in patients with PTSD – a critical overview. Neuroscience. 2014;283:166–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

