GATA3 regulates Th1/Th2 balance in allergic rhinitis by interacting with RUNX1
- PMID: 40748908
- PMCID: PMC12320846
- DOI: 10.1080/20565623.2025.2541503
GATA3 regulates Th1/Th2 balance in allergic rhinitis by interacting with RUNX1
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the action mechanism of GATA3 and Runt-related transcription factor 1(RUNX1) in modulating regulatory the Th1/Th2 cell differentiation and treat allergic rhinitis (AR).
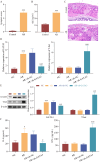
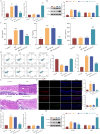
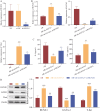
Methods: Established AR model mice by ovalbumin (OVA) and isolated the peripheral blood monocytes (PBMCs), evaluating behavioral changes of AR mice. Analysis of histopathological characteristics by HE. sIgE, IL-4, and IFN-γ were detected by ELISA. RT-qPCR and Western blot detected the expression of GATA3, T-bet, and RUNX1. Using immunofluorescence to detect the expression of GATA and T-bet.
Results: Knockout GATA3 suppressed the expression of GATA3 and concentration of sIgE and IL-4, and promoted the expression of T-bet and concentration of IFN-γ. Knockout GATA3 alleviates inflammation in AR mice by increasing the CD4+ IFN-γ+ cell rate and decreasing the CD4+ IL-4+ cell rate. RUNX1 and GATA3 were both expressed in the nucleus, GATA3 could bind and interact with RUNX1, si-RUNX1 reversed the effect of sh-GATA3, RUNX1 regulated the balance of Th1/Th2 to alleviate inflammation in AR mice by down-regulating expression of GATA3.
Conclusion: GATA3 regulated the balance of Th1/Th2 cells maybe by the interaction between RUNX1 to improve anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory potential strategies in AR therapy.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis (AR); GATA3; Th1/Th2 cell differentiation; inflammation; runt-related transcription factor 1(RUNX1).
Plain language summary
This study examined the role of GATA3 and RUNX1 in allergic rhinitis (AR). The results showed that in AR mice, the expression of GATA3 increases, and inhibiting GATA3 can promote Th1 activation and alleviate the inflammatory response. In addition, GATA3 regulates the balance of Th1/Th2 cells by inhibiting RUNX1. These discoveries suggest that the way GATA3/RUNX1 axis works might be key in causing AR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
