Glia-derived noncanonical fatty acid binding protein modulates brain lipid storage and clearance
- PMID: 40749059
- PMCID: PMC12315990
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv2902
Glia-derived noncanonical fatty acid binding protein modulates brain lipid storage and clearance
Abstract
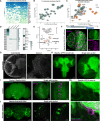
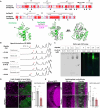
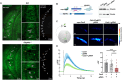
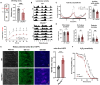
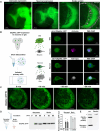
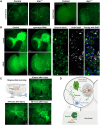
Glia-derived secretory factors are essential for brain development, physiology, and homeostasis, with their dysfunction linked to a variety of neurological disorders. Through genetic and biochemical approaches, we identified odorant binding protein 44a (Obp44a), a noncanonical α-helical fatty acid binding protein (FABP) highly expressed in Drosophila central nervous system glia. Obp44a binds long-chain fatty acids and shuttles between glia and neurons, acting as a secretory lipid chaperone and scavenger to support lipid storage, efflux, and redox homeostasis. Notably, Obp44a is recruited to apoptotic cells and injured axons, especially when glial engulfment is impaired, demonstrating its role in lipid waste management and clearance of cellular debris during development and in pathological states. Our findings highlight FABPs' importance in regulating brain lipid dynamics and neuronal response to stress and injury. By visualizing FABP function in vivo, this study provides insights into how defective lipid regulation may contribute to neuronal stress and disease progression.
Figures

References
-
- Bozek K., Wei Y., Yan Z., Liu X., Xiong J., Sugimoto M., Tomita M., Paabo S., Sherwood C. C., Hof P. R., Ely J. J., Li Y., Steinhauser D., Willmitzer L., Giavalisco P., Khaitovich P., Organization and evolution of brain lipidome revealed by large-scale analysis of human, chimpanzee, macaque, and mouse tissues. Neuron 85, 695–702 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Fitzner D., Bader J. M., Penkert H., Bergner C. G., Su M., Weil M. T., Surma M. A., Mann M., Klose C., Simons M., Cell-type- and brain-region-resolved mouse brain lipidome. Cell Rep. 32, 108132 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Vaughen J. P., Theisen E., Rivas-Serna I. M., Berger A. B., Kalakuntla P., Anreiter I., Mazurak V. C., Rodriguez T. P., Mast J. D., Hartl T., Perlstein E. O., Reimer R. J., Clandinin M. T., Clandinin T. R., Glial control of sphingolipid levels sculpts diurnal remodeling in a circadian circuit. Neuron 110, 3186–3205.e7 (2022). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

