A pan-respiratory virus attachment inhibitor with high potency in human airway models and in vivo
- PMID: 40749064
- PMCID: PMC12315981
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv9311
A pan-respiratory virus attachment inhibitor with high potency in human airway models and in vivo
Abstract
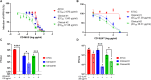
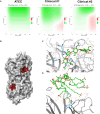
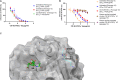
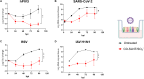
Respiratory viruses can cause severe infections, often leading to hospitalization or death, and pose a major pandemic threat. No broad-spectrum antiviral is currently available. However, most respiratory viruses use sialic acid or heparan sulfates as attachment receptors. Here, we report the identification of a pan-respiratory antiviral strategy based on mimicking both glycans. We synthesized a modified cyclodextrin that simultaneously mimics heparan sulfate and sialic acid. This compound demonstrated broad-spectrum antiviral activity against important human pathogens: parainfluenza virus 3, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza virus H1N1, and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In addition, the compound is active against avian strains of influenza virus, revealing its importance for pandemic preparedness. The compound retains broad-spectrum activity in ex vivo models of respiratory tissues and in vivo against respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus, using prophylactic and therapeutic strategies. These findings contribute to the development of future treatments and preventive measures for respiratory viral infections.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uyeki T. M., Milton S., Abdul Hamid C., Reinoso Webb C., Presley S. M., Shetty V., Rollo S. N., Martinez D. L., Rai S., Gonzales E. R., Kniss K. L., Jang Y., Frederick J. C., De La Cruz J. A., Liddell J., Di H., Kirby M. K., Barnes J. R., Davis C. T., Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus infection in a dairy farm worker. N. Engl. J. Med. 390, 2028–2029 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Morse J., Coyle J., Mikesell L., Stoddard B., Eckel S., Weinberg M., Kuo J., Riner D., Margulieux K., Stricklen J., Dover M., Kniss K. L., Jang Y., Kirby M. K., Frederick J. C., Lacek K. A., Davis C. T., Uyeki T. M., Lyon-Callo S., Bagdasarian N., Influenza A(H5N1) virus infection in two dairy farm workers in Michigan. N. Engl. J. Med. 391, 963–964 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

