The Kelch 3 motif on gigaxonin mediates the interaction with NUDCD3 and regulates vimentin filament morphology
- PMID: 40749357
- PMCID: PMC12403043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2025.151508
The Kelch 3 motif on gigaxonin mediates the interaction with NUDCD3 and regulates vimentin filament morphology
Abstract
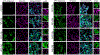
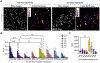
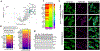
Gigaxonin is an intermediate filament (IF)-interacting partner belonging to the Kelch-like (KLHL) protein family. Gigaxonin is encoded by the KLHL16 gene, which is mutated in Giant Axonal Neuropathy (GAN). The lack of functional gigaxonin in GAN patient cells impairs IF proteostasis by affecting IF protein degradation and transport. This leads to focal abnormal accumulations of IFs and compromised cellular function, with neurons being most severely impacted. We hypothesized that gigaxonin forms molecular interactions via specific sequence motifs to regulate IF proteostasis. The goal of this study was to examine how distinct Kelch motifs on gigaxonin regulate IF protein degradation and filament morphology. We analyzed vimentin IFs in HEK293 cells overexpressing wild type (WT) gigaxonin, or gigaxonin lacking each of the six individual Kelch motifs, K1-K6. All six gigaxonin deletion mutants (ΔK1-ΔK6) promoted the degradation of soluble vimentin. Compared to WT-gigaxonin, ΔK3-gigaxonin exhibited increased soluble vimentin degradation and increased presence of thick bundles of vimentin IFs. The ΔK4 mutant showed similar, but milder phenotypes compared to ΔK3. Using mass spectrometry proteomics we found that, relative to WT gigaxonin, ΔK3 gigaxonin had increased associations with ubiquitination-associated and mitochondrial proteins but lost the association with the NudC domain-containing protein 3 (NUDCD3), a molecular chaperone enriched in the nervous system. AlphaFold modeling revealed loss of gigaxonin-NUDCD3 binding with ΔK3 and altered binding with ΔK4. Collectively, our cell biological data show the induction of an abnormal GAN-like IF phenotype in cells expressing ΔK3- and, to a lesser extent, ΔK4-gigaxonin, while our proteomic profiling links the loss of gigaxonin-NUDCD3 interactions with defective IF proteostasis.
Keywords: Chaperone; Cytoskeleton; Gigaxonin; Intermediate filaments; Kelch domain; NUDCD3; Neurodegenerative disease.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Natasha Snider reports financial support was provided by NIH, Hannah’s Hope Fund, American Heart Association. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
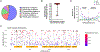

Update of
-
The Kelch 3 motif on gigaxonin mediates the interaction with NUDCD3 and regulates vimentin filament morphology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 13:2025.03.10.641328. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.10.641328. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Eur J Cell Biol. 2025 Sep;104(3):151508. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2025.151508. PMID: 40161598 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Battaglia R, Faridounnia M, Beltran A, Robinson J, Kinghorn K, Ezzell JA, Bharucha-Goebel D, Bonnemann C, Hooper JE, Opal P, Bouldin TW, Armao D, Snider N, 2023. Intermediate filament dysregulation in astrocytes in the human disease model of KLHL16 mutation in giant axonal neuropathy (GAN). Mol Biol Cell 34, mbcE23030094. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bharucha-Goebel DX, Norato G, Saade D, Paredes E, Biancavilla V, Donkervoort S, Kaur R, Lehky T, Fink M, Armao D, Gray SJ, Waite M, Debs S, Averion G, Hu Y, Zein WM, Foley AR, Jain M, Bonnemann CG, 2021. Giant axonal neuropathy: cross-sectional analysis of a large natural history cohort. Brain 144, 3239–3250. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boizot A, Talmat-Amar Y, Morrogh D, Kuntz NL, Halbert C, Chabrol B, Houlden H, Stojkovic T, Schulman BA, Rautenstrauss B, Bomont P, 2014. The instability of the BTB-KELCH protein Gigaxonin causes Giant Axonal Neuropathy and constitutes a new penetrant and specific diagnostic test. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2, 47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bomont P, Cavalier L, Blondeau F, Ben Hamida C, Belal S, Tazir M, Demir E, Topaloglu H, Korinthenberg R, Tuysuz B, Landrieu P, Hentati F, Koenig M, 2000. The gene encoding gigaxonin, a new member of the cytoskeletal BTB/kelch repeat family, is mutated in giant axonal neuropathy. Nat Genet 26, 370–374. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

