Neurofeedback training for executive function in ADHD children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40750997
- PMCID: PMC12316938
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-94242-4
Neurofeedback training for executive function in ADHD children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
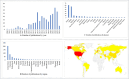
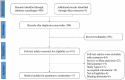
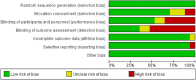
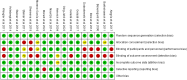
Executive function deficits are commonly observed in children diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This research investigates the effectiveness of neurofeedback training (NFT) in improving executive functions among this group. Studies were meticulously selected following stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria. The quality of these studies was assessed using the PEDro scale. Seventeen RCT studies were identified, totaling 939 participants. We observed significant improvements in global executive function (p < 0.055), inhibitory control (p < 0.0001) and working memory (p < 0.05) following NFT. Notably, NFT exceeding 1,260 min was more effective in enhancing inhibitory control (p < 0.01) and working memory (p < 0.01). Additionally, the effects of NFT on inhibitory control (p = 0.05) and working memory (p < 0.01) were found to be enduring. NFT is an effective intervention for improving inhibitory control and working memory in children with ADHD. Working memory exhibits a more significant enhancement when the duration exceeds 1260 min, while inhibitory control follows closely behind. Moreover, it has a more sustained effect on working memory, alongside a notable albeit secondary effect on inhibitory control.
Keywords: ADHD; Children; Executive function; Meta-analysis; Neurofeedback training.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Parent training interventions for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 7;2011(12):CD003018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003018.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 22161373 Free PMC article.
-
Technological aids for the rehabilitation of memory and executive functioning in children and adolescents with acquired brain injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 1;7(7):CD011020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27364851 Free PMC article.
-
EEG-Guided Adaptive Learning: A New Neuroeducational Approach to the Facilitation of Cognitive Control in ADHD Children.Child Care Health Dev. 2025 Jul;51(4):e70113. doi: 10.1111/cch.70113. Child Care Health Dev. 2025. PMID: 40527858 Clinical Trial.
-
The reading difficulties in Chinese for individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: the role of executive function deficits.PeerJ. 2025 Jul 9;13:e19679. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19679. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40656961 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 25;2015(11):CD009885. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009885.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 27;3:CD009885. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009885.pub3. PMID: 26599576 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Polanczyk, G., de Lima, M. S., Horta, B. L., Biederman, J. & Rohde, L. A. The worldwide prevalence of ADHD: A systematic review and metaregression analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry164, 942–948 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Wang, Y. et al. Connections between the middle frontal gyrus and dorso-ventral attention network associate with the development of attentional symptoms. Biol. PsychiatryS0006–3223, 01291–01295 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Westby, C. & Watson, S. Perspectives on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Executive functions, working memory, and language disabilities. Semin. Speech. Lang.25, 241–254 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Lambek, R. et al. Executive dysfunction in school-age children with ADHD. J. Atten. Disord.15, 646–655 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

