Effects of subanesthetic dose of ketamine on motor and cognitive outcomes of harmaline-induced essential tremor model: a focus on Lingo-1 and inflammatory pathways
- PMID: 40751128
- PMCID: PMC12317601
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-025-00966-4
Effects of subanesthetic dose of ketamine on motor and cognitive outcomes of harmaline-induced essential tremor model: a focus on Lingo-1 and inflammatory pathways
Abstract
Introduction: Essential tremor (ET) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by action tremors and various non-motor symptoms. This study investigated the potential therapeutic effects of ketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist with known GABA modulatory and anti-inflammatory properties, in a harmaline-induced model of ET in mice. We also evaluated the changes in expression of inflammatory interleukin 6 (IL-6) as well as Leucine rich repeat and Immunoglobin-like domain-containing protein 1 (Lingo-1), a prominent gene involved in the pathogenesis of ET.
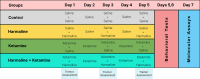
Methods: Male Swiss Webster mice were divided into four groups: control, harmaline (10 mg/kg), ketamine (8 mg/kg), and harmaline + ketamine. Tremor severity, muscle strength, locomotor activity, anxiety-like behavior, and passive avoidance learning were assessed. Cerebellar expression of Lingo-1 and IL-6 was analyzed using real-time PCR.
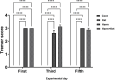
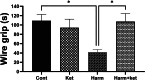
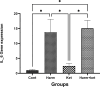
Results: Ketamine did not significantly reduce harmaline-induced tremors but improved muscle strength deficits in the wire grip test. In the open field test, ketamine normalized some harmaline-induced changes in locomotor activity and grooming behavior. No significant differences were observed in passive avoidance learning across groups. At the molecular level, ketamine did not mitigate the harmaline-induced increase in IL-6 expression, and Lingo-1 expression was not significantly altered by either harmaline or ketamine treatment.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that ketamine has limited efficacy in the harmaline ET model, showing some improvements in motor function and anxiety-like behavior but failing to address core tremor symptoms or modulate inflammatory and Lingo-1 pathways. These results highlight the complex nature of ET pathophysiology and the need for further research into targeted therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Essential tremor; Harmaline. Lingo-1; Inflammation; Ketamine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: All experiments were done in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals) NIH Publication No. 80–23, revised 1996). All experiments were performed in accordance with the protocols approved by Kerman University of Medical Sciences Laboratory Animal Care and was accepted by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Kerman University of Medical Sciences (IRB code: IR.KMU.REC.1401.017). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that no conflict of interest in present. The research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Okelberry T, Lyons KE, Pahwa R. Updates in essential tremor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2024:106086. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

