Inhibition of epithelial cell YAP-TEAD/LOX signaling attenuates pulmonary fibrosis in preclinical models
- PMID: 40753090
- PMCID: PMC12318044
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61795-x
Inhibition of epithelial cell YAP-TEAD/LOX signaling attenuates pulmonary fibrosis in preclinical models
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and lethal disease characterized by excessive extracellular matrix deposition. Current IPF therapies slow disease progression but do not stop or reverse it. The (myo)fibroblasts are thought to be the main cellular contributors to excessive extracellular matrix production in IPF. Here we show that fibrotic alveolar type II cells regulate production and crosslinking of extracellular matrix via the co-transcriptional activator YAP. YAP leads to increased expression of Lysl oxidase (LOX) and subsequent LOX-mediated crosslinking by fibrotic alveolar type II cells. Pharmacological YAP inhibition via verteporfin reverses fibrotic alveolar type II cell reprogramming and LOX expression in experimental lung fibrosis in vivo and in human fibrotic tissue ex vivo. We thus identify YAP-TEAD/LOX inhibition in alveolar type II cells as a promising potential therapy for IPF patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

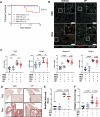
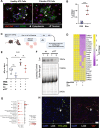
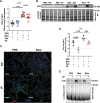
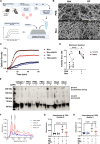
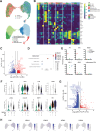
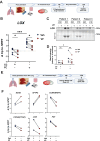
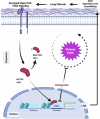
References
-
- Martinez, F. J. et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.3, 17074 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Martinez, F. J. & Lederer, D. J. Focus on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: advancing approaches to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Chest154, 978–979 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Noth, I. & Martinez, F. J. Recent advances in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest132, 637–650 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 805361/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- 2018-02352/Vetenskapsrådet (Swedish Research Council)
- R01 HL146519/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 512453064, BfR 60-0102-01.P588/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- U54 AG075931/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

