Broad neuraminidase antibodies confer protection against seasonal and avian influenza viruses
- PMID: 40753167
- PMCID: PMC12318061
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62040-1
Broad neuraminidase antibodies confer protection against seasonal and avian influenza viruses
Abstract
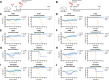
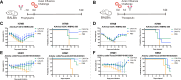
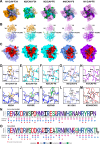
Neuraminidase (NA) is a critical target for universal influenza vaccines and therapeutic antibodies, yet its antigenic landscape remains incompletely understood. Here we identify two broadly cross-protective monoclonal antibodies, CAV-F6 and CAV-F34, from influenza-infected individuals. These antibodies inhibit NA enzymatic activity across multiple subtypes and confer protection against seasonal influenza in female mouse models. Importantly, the two antibodies also neutralize emerging avian strains, including recent bovine H5N1 and H7N9 strains, both with pandemic potential. Structural studies reveal that both antibodies target conserved regions of the NA active site via HCDR3, blocking sialic acid interaction. Furthermore, we observe distinct occupancy for the two antibodies on N2 tetramer, which is likely due to differences in binding affinity. Our findings provide molecular insights into NA-targeted immunity and offer a foundation for developing broadly protective influenza vaccines and therapeutics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zaraket, H., Hurt, A. C., Clinch, B., Barr, I. & Lee, N. Burden of influenza B virus infection and considerations for clinical management. Antivir. Res185, 104970 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

