Isorhamnetin protects against D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury in mice through anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammation, and anti-apoptosis
- PMID: 40753249
- PMCID: PMC12318423
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-025-04949-0
Isorhamnetin protects against D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury in mice through anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammation, and anti-apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Acute liver injury (ALI), which can progress to cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma and acute liver failure, has become a global concern and a serious threat to human life and health. Isorhamnetin (ISO) is an O-methylated flavonol from the class of flavonoids. It has a protective effect on various organs, but its effect on ALI is still unclear in current studies.
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of ISO against D-galactosamine (D-GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI and to explore the underlying molecular mechanisms.
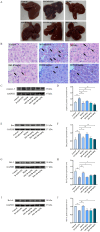
Methods: Ninety-six male Kunming mice were randomly divided into six groups and given the appropriate drug administration for 14 days. The ALI mouse model was established by intraperitoneal injection of 700 mg/kg D-GalN and 10 µg/kg LPS. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was performed to observe the histopathological changes. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and quantitative Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed to detect the expression of genes related to oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflammation and apoptosis related factors were detected by western blot.
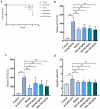
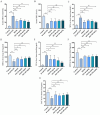
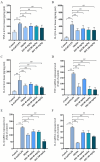
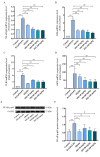
Results: ISO alleviated D-GalN/LPS-induced ALI, reducing the alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (P < 0.01), while improving histopathology (P < 0.05). Additionally, ISO elevated the superoxide dismutase (SOD) level, and improved the survival rate of mice (P < 0.01). Moreover, ISO reduced the nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels (P < 0.05), while increasing the glutathione (GSH), and catalase (CAT) levels (P < 0.05). ISO also decreased the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B alpha (IκBα), Nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) p65, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) at the messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) level (P < 0.05). Furthermore, western blot showed that ISO decreased the expression of NF-κB p-p65, cysteine aspartate protease-3 (caspase-3), and B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein (Bax) proteins and elevated the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and B-cell lymphoma 2-like protein (Bcl-xL) proteins (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: ISO could alleviate D-GalN/LPS-induced ALI by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines, enhancing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins, reducing hepatocyte apoptosis, and inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Our study will provide some new references for treating ALI with ISO.
Keywords: Acute liver injury; Apoptosis; D-GalN/LPS; Inflammatory cytokines; Isorhamnetin; Oxidative stress.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: A total of 96 KM male mice were used in this study, 16 mice per group. This study’s experiments were conducted per the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and in accordance with Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines. The treatment of experimental animals strictly followed the principles of “reduction, refinement, and replacement” and was provided humanely. The procedure used in animal experiments has the approval of the Animal Care Committee at Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, and the ethics approval number is DW20231220-288. Consent for publication: No applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Vasques F, Cavazza A, Bernal W. Acute liver failure. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2022;28(2):198–207. 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000923. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

