Hand Eczema and Facial Skin Problems - Association with Occupational Exposures among Community Care Personnel in Sweden: A Cross-sectional Study
- PMID: 40753480
- PMCID: PMC12340986
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v105.43771
Hand Eczema and Facial Skin Problems - Association with Occupational Exposures among Community Care Personnel in Sweden: A Cross-sectional Study
Abstract
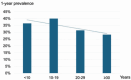
Hand eczema and facial skin problems are common occupational-related skin diseases. However, the data regarding care workers in community care settings are limited. To assess the prevalence and factors associated with hand eczema and facial skin problems among community care personnel, an online questionnaire link was sent to 10,194 personnel in Sweden, with questions regarding hygiene routines, skin problems, and demographics of the participants. Respondents were categorized into groups regarding their skin symptoms. In all, 1,923 (18.9%) responded (89.8% females; 75.9% assistant nurses and care assistants). The 1-year prevalence of hand eczema and facial skin problems was 34.7% and 45.5%, respectively. Dose-dependent associations were found between occupational exposure to soap and water and hand eczema, and duration of face mask use and facial problems. Also, a higher perceived level of stress, female sex, atopic dermatitis, and lower age group were associated with both hand eczema and facial skin problems. In conclusion, healthcare workers in community care have an increased risk of occupationally related skin symptoms, foremost hand eczema, but also facial symptoms related to the use of face masks. Thus, efforts to reduce the harmful effects from the risk factors should be the main concern.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

