Artificial intelligence in orthopedics: fundamentals, current applications, and future perspectives
- PMID: 40754583
- PMCID: PMC12320344
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-025-00633-z
Artificial intelligence in orthopedics: fundamentals, current applications, and future perspectives
Abstract
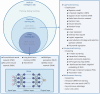
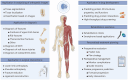
Conventional diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in orthopedics are frequently time intensive and associated with elevated rates of diagnostic error, underscoring the urgent need for more efficient tools to improve the current situation. Recently, artificial intelligence (AI) has been increasingly integrated into orthopedic practice, providing data-driven approaches to support diagnostic and therapeutic processes. With the continuous advancement of AI technologies and their incorporation into routine orthopedic workflows, a comprehensive understanding of AI principles and their clinical applications has become increasingly essential. The review commences with a summary of the core concepts and historical evolution of AI, followed by an examination of machine learning and deep learning frameworks designed for orthopedic clinical and research applications. We then explore various AI-based applications in orthopedics, including image analysis, disease diagnosis, and treatment approaches such as surgical assistance, drug development, rehabilitation support, and personalized therapy. These applications are designed to help researchers and clinicians gain a deeper understanding of the current applications of AI in orthopedics. The review also highlights key challenges and limitations that affect the practical use of AI, such as data quality, model generalizability, and clinical validation. Finally, we discuss possible future directions for improving AI technologies and promoting their safe and effective integration into orthopedic care.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence (AI); Deep learning (DL); Diagnostic; Machine learning (ML); Orthopedics; Therapeutics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rajpurkar P, Chen E, Banerjee O, Topol EJ. AI in health and medicine. Nat Med. 2022;28(1):31–8. - PubMed
-
- Makary MA, Daniel M. Medical error—the third leading cause of death in the US. BMJ. 2016;353:i2139. - PubMed
-
- Xiang Y, Zhao L, Liu Z, Wu X, Chen J, Long E, et al. Implementation of artificial intelligence in medicine: status analysis and development suggestions. Artif Intell Med. 2020;102:101780. - PubMed
-
- Wu E, Wu K, Daneshjou R, Ouyang D, Ho DE, Zou J. How medical AI devices are evaluated: limitations and recommendations from an analysis of FDA approvals. Nat Med. 2021;27(4):582–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources