Function analysis of LIPI-4 in Listeria monocytogenes reveals a key role of flagella formation in the regulation of virulence
- PMID: 40754683
- PMCID: PMC12330269
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2543144
Function analysis of LIPI-4 in Listeria monocytogenes reveals a key role of flagella formation in the regulation of virulence
Abstract
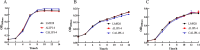
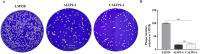
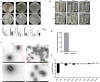
Listeria pathogenicity island 4 (LIPI-4), a newly discovered virulence gene cluster, plays a critical role in the development of central nervous system infections and maternal-fetal infections caused by Listeria monocytogenes. This study aimed to clarify the pathogenic role of LIPI-4 in L. monocytogenes. Our findings revealed that LIPI-4 is involved in the invasion and intracellular proliferation of L. monocytogenes in Caco-2, hCMEC/D3, HTR-8/Svneo, and RAW264.7 cells and facilitates its intercellular migration. Further investigations demonstrated that the deletion of LIPI-4 significantly reduces bacterial motility and impairs flagellum formation. Transcriptomic analysis further indicated that LIPI-4 regulates flagellum formation by modulating microbial metabolic processes and carbon metabolism. Our research demonstrates that LIPI-4 promotes flagellum formation through metabolic regulation, thereby enhancing L. monocytogenes colonization and cellular invasion. This discovery provides novel insights into the pathogenic mechanisms of L. monocytogenes.
Keywords: LIPI-4; Listeria monocytogenes; Virulence; flagella; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

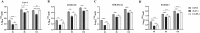

Similar articles
-
Beyond antimicrobial resistance: MATE-type efflux pump FepA contributes to flagellum formation and virulence in Listeria monocytogenes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jul 23;91(7):e0046225. doi: 10.1128/aem.00462-25. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40492698 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity and the prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes in food in Shanghai, China: Insights during 2020-2023 surveillance and the Apriori algorithm approach.Int J Food Microbiol. 2025 Oct 2;441:111323. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2025.111323. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Int J Food Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40543479
-
Interference of the acid stress on the expression of llsX by Listeria monocytogenes pathogenic island 3 (LIPI-3) variants.Food Res Int. 2020 Jun;132:109063. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109063. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32331684
-
Epidemiology of Listeria monocytogenes prevalence in foods, animals and human origin from Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2018 Aug 23;18(1):1057. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5966-8. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30139345 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Tolerance of Listeria monocytogenes to Chemical Oxidants: Comparative Analysis of Transcriptomic Studies.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 Sep;24(5):e70260. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70260. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 40843964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
