[Comparison of efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium fiber laser enucleation of prostate in patients with different prostate volumes]
- PMID: 40754908
- PMCID: PMC12330954
- DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.013
[Comparison of efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium fiber laser enucleation of prostate in patients with different prostate volumes]
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of thulium fiber laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuFLEP) in the treatment of oversized (>200 mL) prostate.
Methods: Clinical data of 475 benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) patients operated by the same urologist at Peking University First Hospital from January 2022 to May 2024 were retrospectively analyzed, all of whom were treated with thulium fiber laser, and the patients were divided into three groups according to the total volume of the prostate (TPV): group A (TPV < 100 mL), group B (100 mL≤TPV < 200 mL), and group C (TPV≥200 mL). The age of the patients in the three groups [(69.38±7.79) years, (69.64±8.69) years, (70.32±7.44) years], International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) [(22.7±1.9), (22.8±2.7), (25.8±3.7)], and the maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) [(7.9±2.7) mL/s, (9.3±4.3) mL/s, (9.9±3.3) mL/s] were not statistically significant (P>0.05). The prostate volume in the three groups [(103.49±46.19) mL, (75.73±30.69) mL, (273.49±49.19) mL] and prostate specific antigen (PSA) [3.52 (1.05, 8.76) μg/L, 6.78 (1.61, 7.45) μg/L, 8.52 (5.05, 12.76) μg/L] were statistically significant (P < 0.05).
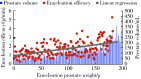
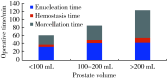
Results: All surgeries were successfully completed. The dif-ferences in enucleation time [30.0 (21.2, 44.5) min, 41.6 (31.2, 52.5) min, 45.1 (35.2, 50.0) min] and hospitalization time [(6.06±1.21) d, (6.15±1.50) d, (7.71±1.74) d] among the three groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05); and the differences in the postoperative indwelling catheter time [(4.0±1.4) d, (4.0±1.3) d, (6.6±1.1) d], operative time [61 (42, 89) min, 82 (62, 105) min, 115 (96, 142) min], enucleation efficiency [1.29 (0.71, 1.56) g/min, 1.67 (1.23, 2.15) g/min, 2.74 (2.20, 3.34) g/min], and hemoglobin drop values [12 (7, 19) g/L, 17 (11, 24) g/L, 27 (19, 35) g/L] were statistically different (P < 0.05). Linear regression ana-lysis was used to show a strong positive linear correlation between enucleation efficiency and enucleation weight (r=0.880, P < 0.001), and the enucleation efficiency increased with the increase of prostate volume. The differences in IPSS [(6.6±1.7), (6.2±1.4), (4.6±1.1)] and Qmax [(18.9±3.1) mL/s, (16.8±3.8) mL/s, (22.9±7.1) mL/s] were not statistically significant among the three groups (P>0.05), and the differences in IPSS and Qmax were statistically significant compared with those before surgery. The differences were statistically significant in preoperative comparisons, but the postoperative urinary flow rate of group C increased significantly more than the remaining two groups in terms of Qmax (P < 0.05). The patients in the three groups were followed up for 3 months, and post-operative complications were categorized into Clavien-Dindo Ⅰ (urinary retention, persistent hematu-ria), Clavien-Dindo Ⅱ (glandular remnants, urinary tract infection, blood transfusion) and Clavien-Dindo Ⅲ (urethral stenosis, contracture of the bladder neck, and reoperation for hemorrhage) based on the Clavien-Dindo Complications System score, the incidence of Clavien-Dindo in the three groups was 5.2% (13 cases), 6.7% (12 cases) and 12.1% (7 cases), respectively, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05); among them, there were statistically significant differences in urinary infection, blood transfusion and bleeding reoperation (P < 0.05), and there was no statistically significant difference in the remaining complications (P>0.05).
Conclusion: The risk of blood transfusion and re-hemostasis increases with larger prostate volume, the efficiency of enucleation increases with the increase of prostate vo-lume, and thulium fiber laser prostate enucleation is safe and effective in the treatment of large-volume BPH.
目的: 评估采用光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术(thulium fiber laser enucleation of the prostate,ThuFLEP)治疗超大体积(>200 mL)前列腺的有效性和安全性。
方法: 回顾性分析2022年1月至2024年5月,于北京大学第一医院由同一泌尿外科医师进行手术的485例良性前列腺增生(benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH)患者的临床资料,患者均采用光纤铥激光,根据前列腺总体积(total volume of the prostate,TPV)将患者分为三组:A组TPV < 100 mL、B组100 mL≤TPV < 200 mL、C组TPV≥200 mL。三组患者的年龄[(69.38±7.79)岁、(69.64±8.69)岁、(70.32±7.44)岁]、国际前列腺症状评分(International Prostate Symptom Score,IPSS)[(22.7±1.9)分、(22.8±2.7)分、(25.8±3.7)分]、最大尿流率(maximum urinary flow rate,Qmax)[(7.9±2.7) mL/s、(9.3±4.3) mL/s、(9.9±3.3) mL/s]差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);三组患者的前列腺体积[(103.49±46.19) mL、(75.73±30.69) mL、(273.49±49.19) mL]、前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen, PSA)[3.52 (1.05, 8.76) μg/L、6.78 (1.61, 7.45) μg/L、8.52 (5.05, 12.76) μg/L]差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
结果: 所有患者的手术均顺利完成,三组患者的剜除时间[30.0 (21.2, 44.5) min、41.6 (31.2, 52.5) min、45.1 (35.2, 50.0) min]、住院时间[(6.06±1.21) d、(6.15±1.50) d、(7.71±1.74) d]差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);而三组患者的术后留置导尿管时间[(4.0±1.4) d、(4.0±1.3) d、(6.6±1.1) d]、手术时间[61 (42, 89) min、82 (62, 105) min、115 (96, 142) min]、剜除效率[1.29 (0.71, 1.56) g/min、1.67 (1.23, 2.15) g/min、2.74 (2.20, 3.34) g/min]、血红蛋白下降值[12 (7, 19) g/L、17 (11, 24) g/L、27 (19, 35) g/L]差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。线性回归分析显示,剜除效率与剜除重量之间存在较强的正向线性相关(r=0.880,P < 0.001),剜除效率随着前列腺体积增加而提高。术后三组患者之间的IPSS[(6.6±1.7)分、(6.2±1.4)分、(4.6±1.1)分]、Qmax[(18.9±3.1) mL/s、(16.8±3.8) mL/s、(22.9±7.1) mL/s]差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后的IPSS、Qmax与术前比较差异均有统计学意义,但术后C组Qmax的提高明显高于其他两组(P < 0.05)。术后并发症以Clavien-Dindo并发症系统评分为标准,分为Clavien-Dindo Ⅰ (尿潴留、持续性血尿)、Clavien-Dindo Ⅱ (腺体残余、泌尿系感染、输血)和Clavien-Dindo Ⅲ (尿道狭窄、膀胱颈挛缩、出血并再次手术),三组患者术后均随访3个月,Clavien-Dindo的并发症发生率分别为5.2% (13例)、6.7% (12例)和12.1% (7例),组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),其中,泌尿系感染、输血及出血并再次手术的组间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),其他并发症的组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
结论: 前列腺体积越大,输血及再次手术的风险增高,剜除效率随着前列腺体积的增加而提高,光纤铥激光前列腺剜除术治疗超大体积的BPH安全、有效。
Keywords: Enucleation; Postoperative complications; Prostatic hyperplasia; Thulium fiber laser.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
"Double rings" En-bloc technique with early anatomical apical release in thuflep for the patients with large glands (≥ 80 mL): the outcomes from single center.BMC Urol. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12894-025-01851-2. BMC Urol. 2025. PMID: 40618135 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of new surgical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia: systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMJ. 2019 Nov 14;367:l5919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l5919. BMJ. 2019. PMID: 31727627 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of 450 nm blue-laser vaporization versus transurethral plasma kinetic enucleation of the prostate (TUPKEP) for benign prostatic hyperplasia in high-risk elderly patients: a focus on safety, efficacy, and sexual function preservation.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Jun 23;40(1):294. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04547-z. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40549059
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of transurethral prostate blue laser vaporization versus green laser vaporization in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with different prostate volumes: A retrospective comparative study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 11;104(28):e43304. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043304. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40660531 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transurethral thulium laser enucleation versus robot-assisted prostatectomy for large-volume benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Robot Surg. 2023 Dec;17(6):2633-2646. doi: 10.1007/s11701-023-01715-7. Epub 2023 Sep 20. J Robot Surg. 2023. PMID: 37731152
References
-
- Baboudjian M, Hashim H, Bhatt N, et al. Summary paper on underactive bladder from the European Association of Urology guidelines on non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms. Eur Urol. 2024;86(3):213–220. - PubMed
-
- Tallè M, Giulioni C, Papaveri A, et al. Influence of preoperative indwelling urinary catheter on outcomes of high-power holmium laser enucleation for very large prostate (≥ 200 mL) World J Urol. 2025;43(1):223–229. - PubMed
-
- Gabrielson AT, Tanidir Y, Castellani D, et al. A global survey of ergonomics practice patterns and rates of musculoskeletal pain among urologists performing retrograde intrarenal surgery. J Endourol. 2022;36(9):1168–1176. - PubMed
-
- Doizi S. Lasers for benign prostatic hyperplasia (hybrid, blue diode, TFL, Moses). Which one to choose? Curr Opin Urol. 2022;32(4):438–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous