[Protective effect of knock-down the expression of Blimp1 gene on early liver injury in CCl4-induced mouse model of liver fibrosis]
- PMID: 40754911
- PMCID: PMC12330913
- DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2025.04.016
[Protective effect of knock-down the expression of Blimp1 gene on early liver injury in CCl4-induced mouse model of liver fibrosis]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the protective effect of knock-down the expression of B lymphocyte induced maturation protein 1 (Blimp1) gene on early liver injury in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced mouse model of liver fibrosis.
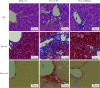
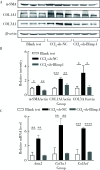
Methods: C57BL/6 mice were intraderitoneal injected with 5% CCl4 olive oil solution to create mouse model of hepatic fibrosis. The expression of Blimp1 gene in the mice was reduced by intraderitoneal injection of short hairpin RNA (shRNA) adeno-associated virus (AAV). The mice were randomly divided into 3 groups: blank test group (n=10), CCl4+AAV-shRNA-NC group (n=10) and CCl4+AAV-shRNA-Blimp1 group (n=10). After 27 days of preparation of the CCl4 mouse model, animal materials were carried out. Western blot and real-time PCR were used to detect the levels of Blimp1, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen type Ⅰ alpha 1 (COL1A1), collagen type Ⅲ alpha 1 (COL3A1), and their mRNA expression levels of liver tissue in each group. The serum of each group was separated to measure aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) by automatic biochemical analyzer. The pathological changes of liver tissue and the degree of liver fibrosis in the mice were detected by pathological staining including hematoxylin-eosin staining, Masson, and Sirius red.
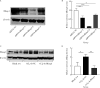
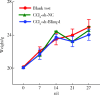
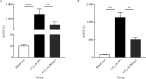
Results: The expression levels of Blimp1 protein in the liver of CCl4+AAV-shRNA-NC group (2.036±0.244, t=3.690, P=0.002) were significantly increased than that of the blank test group. In the CCl4+AAV-shRNA-Blimp1 group, the expression of Blimp1 protein decreased to the basal level (0.783±0.249, t=6.223, P=0.003). Compared with the serum levels of ALT [(1 957.8±633.6) U/L] and AST [(1 808.8±260.1) U/L] in the CCl4+AAV-shRNA-NC group, the serum levels of ALT [(894.0±360.1) U/L, t=3.998, P=0.003] and AST [(820.0±100.6) U/L, t=6.141, P=0.004] in the CCl4+AAV-shRNA-Blimp1 group were significantly decreased. The pathological results of the CCl4+AAV-shRNA-Blimp1 group showed that compared with the CCl4+AAV-shRNA-NC group, the infiltration of inflammatory cells in the liver tissue was reduced and the degree of fibrosis was alleviated. The level of α-SMA (0.676±0.064, t=7.930, P=0.001), COL1A1 (1.426±0.143, t=6.364, P=0.003) and COL3A1 (1.124±0.198, t=3.440, P=0.026) of liver in the CCl4+AAV-shRNA-Blimp1 group were significantly decreased than that of CCl4+AAV-shRNA-NC group, and the mRNA expression levels were altered as well as their protein levels.
Conclusion: Blimp1 plays an important role in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice, and knock-down the expression of Blimp1 gene is beneficial to protect early liver injury in mice.
目的: 探讨敲减转录因子B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1(B lymphocyte induced maturation protein 1, Blimp1)基因对四氯化碳(carbon tetrachloride, CCl4)诱导的小鼠肝纤维化模型早期肝损伤的保护作用。
方法: 采用C57BL/6小鼠腹腔注射5%(体积分数)CCl4橄榄油溶液制备肝纤维化小鼠模型,采用小鼠腹腔注射短发夹RNA (short hairpin RNA, shRNA)腺相关病毒(adeno-associated virus, AAV)敲减Blimp1基因表达。将小鼠随机分为3组,空白实验组(n=10),无意义RNA对照组(n=10)和Blimp1敲减组(n=10)。CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化模型制备27 d后取材,通过Western blot和real-time PCR检测小鼠肝组织Blimp1蛋白、α平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-smooth muscle actin, α-SMA)、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白(collagen type Ⅰ alpha 1, COL1A1)、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白(collagen type Ⅲ alpha 1, COL3A1)及其mRNA表达水平;测定各组小鼠血清中天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate transaminase, AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine transaminase, ALT)水平;采用苏木素-伊红染色、Masson染色和天狼星红染色法鉴定小鼠肝组织的病理变化及肝纤维化程度。
结果: 与空白实验组相比,无意义RNA对照组小鼠肝脏Blimp1蛋白表达水平显著升高(2.036±0.244, t=3.690, P=0.002),Blimp1敲减组小鼠Blimp1蛋白表达降低至基础水平(0.783±0.249, t=6.223, P=0.003)。与无意义RNA对照组小鼠血清ALT [(1 957.8±633.6) U/L]和AST [(1 808.8±260.1) U/L]相比,Blimp1敲减组小鼠血清ALT [(894.0±360.1) U/L, t=3.998, P=0.003]和AST [(820.0±100.6) U/L, t=6.141, P=0.004]水平均显著降低,肝组织炎性细胞浸润减少、纤维化程度减轻,肝脏α-SMA(0.676±0.064, t=7.930, P=0.001)、COL1A1(1.426±0.143, t=6.364, P=0.003)、COL3A1(1.124±0.198, t=3.440, P=0.026)蛋白表达水平降低,且mRNA表达与蛋白水平变化一致。
结论: Blimp1在CCl4诱导的小鼠肝纤维化中发挥重要作用,敲减Blimp1表达有利于保护小鼠的早期肝损伤。
Keywords: Animal models; B lymphocyte induced maturation protein 1; Liver fibrosis; Liver injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Research on the mechanism of gentiopicroside preventing macrophage-mediated liver fibrosis by regulating the MIF-SPP1 signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jul;41(7):593-602. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40620116 Chinese.
-
Leonurine Attenuates CCl4-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Mice via the Hippo-YAP Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 30;19:6553-6571. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S518793. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40761670 Free PMC article.
-
[LncRNA-UCA1-microRNA-143-Notch1 regulates autophagy in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury induced by cardiopulmonary bypass].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Jun;37(6):576-582. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240329-00298. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40820534 Chinese.
-
The intervention of curcumin on rodent models of hepatic fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 May 23;19(5):e0304176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304176. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38781262 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
-
- Marcellin P, Kutala BK. Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver Int. 2018;38(Suppl 1):2–6. - PubMed
-
- Rockey DC, Bell PD, Hill JA. Fibrosis: A common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(12):1138–1149. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro-Shelef M, Lin KI, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, et al. Blimp-1 is required for the formation of immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and pre-plasma memory B cells. Immunity. 2003;19(4):607–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
