Multiparametric Characterization of Individual Suspended Nanoparticles Using Confocal Fluorescence and Interferometric Scattering Microscopy with Microfluidic Confinement
- PMID: 40755002
- PMCID: PMC12356074
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5c02232
Multiparametric Characterization of Individual Suspended Nanoparticles Using Confocal Fluorescence and Interferometric Scattering Microscopy with Microfluidic Confinement
Abstract
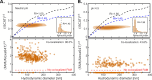
Detailed characterization of the size, mass, payload, and structure of suspended mRNA-lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) is necessary to improve our understanding of how these heterogeneous properties influence therapeutic efficacy and potency. Methods currently in use face limitations in reporting ensemble-average particle properties or requiring dedicated home-built microscopes that are beyond the reach of nanoparticle developers. In this work, we overcome these limitations by combining a commercially available confocal microscope and a convex lens-induced confinement (CLiC) instrument to achieve simultaneous characterization and correlation of the size, mass, refractive index, and nucleic acid payload of individual LNPs. We established the accuracy and precision of our method using nanosized beads and used it to investigate the size, payload, and water content of LNPs in different solvent pH. By employing readily available microscopy tools, we open the door to widespread adoption of our quantitative, in-solution nanoparticle characterization method.
Keywords: confocal microscopy; convex-lens induced confinement; fluorescence; interferometric scattering; lipid nanoparticles; payload; size.
Figures



References
-
- Zhu S., Ma L., Wang S., Chen C., Zhang W., Yang L., Hang W., Nolan J. P., Wu L., Yan X.. Light-scattering detection below the level of single fluorescent molecules for high-resolution characterization of functional nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2014;8(10):10998–11006. doi: 10.1021/nn505162u. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

