Recent Advances in Membrane-Coated Micro/Nanomotors in Biological Applications
- PMID: 40755462
- PMCID: PMC12315904
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S526671
Recent Advances in Membrane-Coated Micro/Nanomotors in Biological Applications
Abstract
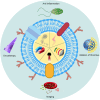
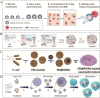
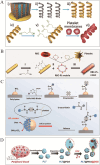
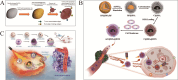
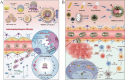
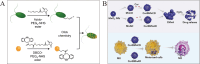
The integration of synthetic micro/nanomotors (MNMs) with natural biomaterials derived from cell membranes has emerged as a highly promising strategy for advancing biological applications. The membrane-coated MNM offers distinct advantages over earlier MNMs dependent on chemical fuels such as hydrogen peroxide, which were prone to poor biocompatibility and harmful byproducts. These include enhanced biocompatibility, immune evasion via natural membrane surfaces, multifunctionality for drug delivery, self-propulsion in complex environments, self-degradation to reduce residual toxicity and inherent imaging capabilities enabling real-time tracking. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the integration of various types of micromotors with natural cell membranes commonly present in the circulatory system. Additionally, it summarizes the methodologies for the preparation, characterization and functional evaluation of biofilm-modified micromotors. The present article also critically examines current developments in biofilm-modified micromotors, addressing their challenges and limitations in enhancing clinical efficacy and facilitating transition to clinical trials in humans.
Keywords: drug delivery; membrane-coated; micro/nanomotors; nanodrugs; self-propulsion.
© 2025 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest for publication in this journal.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cell and cellular component based micro/nanomotors.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jul 13:S1742-7061(25)00519-7. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.07.022. Online ahead of print. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40664295 Review.
-
Photothermal-driven micro/nanomotors: From structural design to potential applications.Acta Biomater. 2024 Jan 1;173:1-35. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.11.018. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 37967696
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
[Research progress of peptide recognition-guided strategies for exosome isolation and enrichment].Se Pu. 2025 May;43(5):446-454. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.10015. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40331609 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

