Rivaroxaban Ameliorates Sunitinib-Induced Injury of Cardiomyocytes via Repressing MAPK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 40755506
- PMCID: PMC12316504
- DOI: 10.1155/cdr/2208110
Rivaroxaban Ameliorates Sunitinib-Induced Injury of Cardiomyocytes via Repressing MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
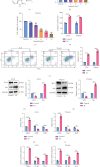
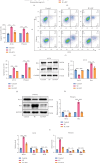
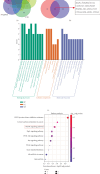
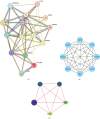
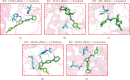
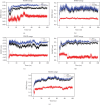
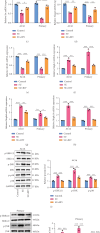
Background: Sunitinib (SU) is used to treat kidney cancer. However, it can also cause cardiotoxicity. This study is performed to investigate whether rivaroxaban (RIV) attenuates SU-induced cardiotoxicity (SIC). Methods and Materials: AC16 cells and primary cardiomyocytes of neonatal mouse were treated with different concentrations (2-10 μM) of SU for 24 h or with 6 μM SU and 10 μg/mL RIV for 24 h. The viability of cardiomyocytes was evaluated using the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and the apoptosis rate was evaluated using flow cytometry. The activity of caspase-3 was determined. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were also measured. The potential targets and downstream pathways of RIV in SIC treatment were investigated using network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. qPCR and western blotting were used to detect the regulatory effects of SU and RIV on mRNA and protein expression of MAPK pathway-related genes, respectively. Results: RIV treatment alleviated SU-induced cardiomyocyte injury by promoting viability and inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress, and the inflammatory response in AC16 cells and primary cardiomyocytes. Caspase 3 (CASP3), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), SRC proto-oncogene, nonreceptor tyrosine kinase (SRC), ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2), and ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 (ABCB1) were candidate targets of RIV in SIC. The binding affinities between RIV and CASP3, STAT3, SRC, ABCG2, and ABCB1 were all less than -7.5 kcal/mol, indicating that RIV could bind stably to these targets. Bioinformatics analyses suggested that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway was involved in the mechanism by which RIV alleviated SIC. RIV treatment decreased the mRNA expression of CASP3 and increased the mRNA expression of STAT3, SRC, ABCG2, and ABCB1 in AC16 cells and primary cardiomyocytes. RIV also inhibited the SU-induced activation of the MAPK pathway. Conclusion: RIV exerts a protective effect against SU-induced cardiomyocyte injury by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway. RIV therapy may be a promising strategy to inhibit SU's cardiotoxicity in cancer patients.
Keywords: MAPK pathway; cardiomyocytes; rivaroxaban; sunitinib.
Copyright © 2025 Ying Qian and Fang Yi. Cardiovascular Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology and experimental verification: Rosmarinic acid alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by regulating BCL2L1.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2025 Jan-Dec;44:9603271251354890. doi: 10.1177/09603271251354890. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40600628
-
The mechanistic study of quercetin in the treatment of alcoholic brain injury via the JNK/P38 MAPK signaling pathway.Apoptosis. 2025 Aug;30(7-8):1875-1892. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02125-w. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40457147
-
The VDAC3/DHODH Axis Ameliorates Sepsis-induced Myocardial Injury by Regulating Ferroptosis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Jun 17;30(6):39559. doi: 10.31083/FBL39559. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 40613295
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
