Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A French Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 40755508
- PMCID: PMC12316348
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001851
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A French Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) are at elevated risk of malignancy. Data on the safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in this population remain limited. We aimed to reassess the benefit-risk profile of ICI therapy in KTRs using a multicenter cohort, in the recent era.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of all KTRs treated with ICIs for advanced or metastatic cancer, across 6 transplant centers. We evaluated cancer response, acute rejection (AR) incidence, graft survival, and patient survival.
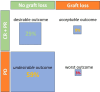
Results: From 2015 to 2024, 34 KTRs were analyzed. The most common cancers were cutaneous (56%) and non-small cell lung cancer (32%). Pembrolizumab was the most used ICI (53%). The objective response rate was 38%, with a median progression-free survival of 5.5 mo and an overall survival of 10.7 mo. Biopsy-proven AR occurred in 26.5% of patients, at a median time of 52 d after ICI start. All rejection episodes involved T cells, and one-third showed additional humoral features. No clinical predictors of AR were identified. Among all patients, 29% had a favorable outcome (tumor response without ICI-induced graft loss), 12% experienced a tumor response with graft loss, 59% had progression disease without graft loss, and 3% experienced the worst outcome (progression disease with graft loss).
Conclusions: Our study suggests that ICI therapy is a viable option for KTRs with poor-prognosis cancers, demonstrating a 38% tumor response rate and a lower incidence of graft loss (15%) compared with previously reported rates. Prospective studies are needed to optimize the use of ICI in KTRs.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no funding or conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Delyon J, Zuber J, Dorent R, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in transplantation—a case series and comprehensive review of current knowledge. Transplantation. 2021;105:67–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

