Paraspinal Extramedullary Hematopoiesis in a Transfusion-Dependent Beta-Thalassemia Patient: A Case Report
- PMID: 40755700
- PMCID: PMC12318370
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87271
Paraspinal Extramedullary Hematopoiesis in a Transfusion-Dependent Beta-Thalassemia Patient: A Case Report
Abstract
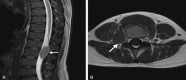
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH) is a compensatory mechanism in chronic anemias, such as transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia (TDT), most commonly affecting the liver and spleen. Paraspinal EMH is rare and may lead to spinal cord compression, resulting in neurological deficits. We present a 26-year-old male patient with longstanding TDT who developed progressive bilateral lower limb weakness, pelvic paresthesia, and acute urinary retention. MRI revealed a bilateral paraspinal mass compressing the dural sac and spinal cord, with concurrent severe myocardial and hepatic iron overload. Given the high operative risk and contraindications to surgery and radiotherapy, treatment included hypertransfusion, dual iron chelation therapy, and hydroxyurea. The patient developed hydroxyurea-induced bone marrow aplasia requiring discontinuation of treatment. Over six months, motor and sensory functions improved, bladder function partially recovered, iron markers decreased, and MRI showed regression of the mass. This case highlights the complexities in diagnosing and managing paraspinal EMH in high-risk TDT patients and supports the effectiveness of individualized conservative therapy.
Keywords: beta-thalassemia; extramedullary hematopoiesis; hydroxyurea; hypertransfusion; iron chelation; paraspinal mass; spinal cord compression.
Copyright © 2025, Rawashdeh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurological Complications in a Patient With Thalassemia Intermedia and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Case of Extramedullary Hematopoiesis-Induced Spinal Cord Compression.Cureus. 2025 May 26;17(5):e84844. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84844. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40568257 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-Thalassemia.2000 Sep 28 [updated 2024 Feb 8]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2000 Sep 28 [updated 2024 Feb 8]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301599 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Epidural Spinal Cord Compression due to Extramedullary Hematopoiesis: Systematic Review of the Literature with an Illustrative Case.World Neurosurg. 2025 Jan;193:119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.10.034. Epub 2024 Nov 9. World Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 39427876
-
Calcium channel blockers for preventing cardiomyopathy due to iron overload in people with transfusion-dependent beta thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 17;11(11):CD011626. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011626.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37975597 Free PMC article.
-
Desferrioxamine mesylate for managing transfusional iron overload in people with transfusion-dependent thalassaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 21;2013(8):CD004450. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004450.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23963793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- β-thalassemia. Rund D, Rachmilewitz E. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1135–1146. - PubMed
-
- Images in clinical medicine. Extramedullary hematopoiesis in thalassemia. Hassanzadeh M. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1252. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines for diagnosis and management of beta-thalassemia intermedia. Karimi M, Cohan N, De Sanctis V, Mallat NS, Taher A. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014;31:583–596. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
