Exploring of bladder cancer immune-related genes and potential therapeutic targets based on transcriptomic data and Mendelian randomization analysis
- PMID: 40755754
- PMCID: PMC12313568
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1607098
Exploring of bladder cancer immune-related genes and potential therapeutic targets based on transcriptomic data and Mendelian randomization analysis
Abstract
Background: Despite advancements in clinical treatment modalities, immune-related molecular mechanisms underlying bladder cancer remain unclear. Therefore, this study aimed to identify immune-related biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for bladder cancer, thereby contributing to the development of novel therapeutic interventions.
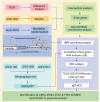
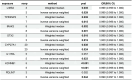
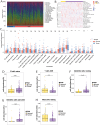
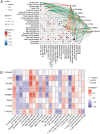
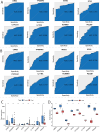
Methods: By integrating data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and genome-wide association study (GWAS) databases, combined with differential expression analysis, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and Mendelian randomization analysis, key immune-related genes in bladder cancer were identified. The correlation between these key genes and immune cell infiltration was also analyzed. The diagnostic efficacy of the key genes was evaluated using Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves and validated using independent public datasets. Finally, Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to confirm the potential value of these molecular markers in bladder cancer.
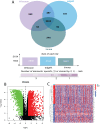
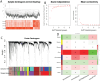
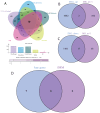
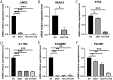
Results: Differential expression analysis revealed 2,033 bladder cancer-related genes. WGCNA identified 1,391 immune-related genes and Mendelian randomization analysis identified 187 candidate genes with causal relationships. Eight significantly downregulated genes were identified: LIMS2, TP53INP2, IRAK3, STX2, CYP27A1, IL11RA, KCNMB1, and PDLM7. These genes were significantly associated with immune cell infiltration and exhibited good diagnostic efficacy, as demonstrated by ROC curve analysis and validated in independent public datasets. Furthermore, qRT-PCR experiments showed that LIMS2, IRAK3, STX2, IL11RA, KCNMB1, and PDLM7 were significantly downregulated in the tumor group, consistent with the bioinformatic analysis results, suggesting their potential clinical value.
Conclusion: This study identified six immunoregulatory genes that were significantly negatively associated with bladder cancer risk. These genes may serve not only as potential biomarkers for bladder cancer immunity but also contribute to a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms of bladder cancer.
Keywords: CIBERSORT; Mendelian randomization analysis; WGCNA; biomarkers; bladder cancer; potential therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Yang, Ma, Tao, He, Wu, Zhao, Niu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

