Mouse B cells engineered to express an anti-HPV antibody elicit anti-tumor T cell responses
- PMID: 40755763
- PMCID: PMC12313569
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1613879
Mouse B cells engineered to express an anti-HPV antibody elicit anti-tumor T cell responses
Abstract
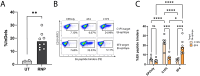
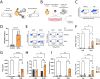
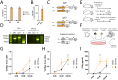
Transplantation of engineered B cells has demonstrated efficacy in HIV disease models. B cell engineering may also be utilized for the treatment of cancer. Recent studies have highlighted that B cell activity is associated with favorable clinical outcomes in oncology. In mice, polyclonal B cells have been shown to elicit anti-cancer responses. As a potential novel cell therapy, we demonstrate that engineering B cells to target a tumor-associated antigen enhances polyclonal anti-tumor responses. We observe that engineered B cells expressing an anti-HPV B cell receptor internalize the antigen, enabling subsequent activation of oncoantigen-specific T cells. Secreted antibodies from engineered B cells form immune complexes, which are taken up by antigen-presenting cells to further promote T cell activation. Engineered B cells hold promise as novel, multi-modal cell therapies and open new avenues in solid tumor targeting.
Keywords: B cell; antibody; cancer; cell engineering; cell therapy (CT); genome editing; tertiary lymphoid structures.
Copyright © 2025 Guberman Bracha, Biber, Zelikson, Shavit, Avraham, Vagima, Bublik, Katz, Barzel, Klapper, Hess and Nahmad.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors MG, GB, SS, RA, YV, DB, YK, LK, SH, and AN were employed by the company Tabby Therapeutics Ltd, Israel. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Näsman A, Du J, Dalianis T. A global epidemic increase of an HPV-induced tonsil and tongue base cancer – potential benefit from a pan-gender use of HPV vaccine. J Intern Med. (2020) 287(2):134–52., PMID: - PubMed
-
- Ramos da Silva J, Bitencourt Rodrigues K, Formoso Pelegrin G, Silva Sales N, Muramatsu H, de Oliveira Silva M, et al. Single immunizations of self-amplifying or non-replicating mRNA-LNP vaccines control HPV-associated tumors in mice. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15(686):eabn3464. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn3464, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

