Imidazolium salts carrying two positive charges: design, synthesis, characterization, molecular docking, antibacterial and enzyme inhibitory activities
- PMID: 40756032
- PMCID: PMC12313567
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1579916
Imidazolium salts carrying two positive charges: design, synthesis, characterization, molecular docking, antibacterial and enzyme inhibitory activities
Abstract
Introduction: The discovery of alternative drugs has gained importance due to the many side effects of these drugs used for treatment.
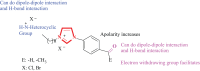
Methods: Herein, the synthesis of a series of unsymmetrical imidazolium salts containing 4-acetylphenyl/4-formylphenyl and bioactive heterocyclic groups such as morpholine, piperidine, pyrrole or pyridine was reported. 4-(1-H-imidazol-1-yl)acetophenone and 4-(1-H-imidazol-1-yl)benzaldehyde were used as salt precursors. Alkyl halides containing heterocyclic groups such as 2-morpholinoethyl hydrochloride, 2-pyrrolidinoethyl hydrochloride, 2-piperidinoethyl hydrochloride and pyridin-2-ylmethyl bromide hydrobromide were used. Thus, there are two positively charged nitrogens in the structure of these salts synthesized by the quaternization method. The structures of all salts were fully characterized by 1H, 13C NMR, FTIR spectroscopic and elemental analysis methods. the a series of imidazolium salts (1a-d and 2a-d) were designed, synthesized and fully characterized by spectroscopic methods.
Results: The inhibitory effect against AChE of the series compounds was evaluated as in vitro and in silico studies. The results indicated that the compounds showed remarkably potent inhibitory effects on AChE with K I values ranging from 0.63 ± 0.04 μM to 11.23 ± 1.05 μM and IC50 values spanning from 0.82 ± 0.06 μM to 14.75 ± 0.82 μM. The antimicrobial activities of the synthesized compounds were measured by inhibition of bacterial growth expressed as minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values. It was observed that the synthesized compounds exhibited antimicrobial activity especially against Gram negative bacteria. In addition, the results of molecular docking studies of bacteria supported our antimicrobial results.
Conclusions: The results suggested that the synthesized compounds showed the potential to be antimicrobial and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Keywords: N-heterocyclic carbene; acetylcholinesterase; anti-Alzheimer; antimicrobial; imidazolium salt.
Copyright © 2025 Demirhan, Necip, Oner, Gumuscu, Demirci, Gok, Doni, Işık, Rudrapal, Khan and Ibrahim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






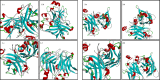

References
-
- Aktas A., Keles Temur U., Gok Y., Balcıoglu S., Ates B., Aygün M. (2018). 2- Morpholinoethyl-substituted N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) precursors and their silver(I)NHC complexes: synthesis, crystal structure and in vitro anticancer properties. J. Iran. Chem. Soc 15, 131–139. doi: 10.1007/s13738-017-1216-8 - DOI
-
- Arduengo A. J., Calabrese J. C., Davidson F., Rasika, Dias H. V., Goerlich J. R., et al. (1999). C–H insertion reactions of nucleophilic carbenes. Helv Chim. Acta 82, 2348–2364.
-
- Ardugenyo A. J., Krafczyk R., Schmutzler R., Craig H. A. (1999). Imidazolylidenes, imidazolinylidenes and imidazolidines. Tetrah. 55, 14523–14534. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(99)00927-8 - DOI
-
- Bal S., Demirci Ö., Şen B., Taslimi P., Aktaş A., Gök Y., et al. (2021). Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure, α-glycosidase, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties of 1, 3-disubstituted benzimidazolium salts. Arch. Phar. 354, 2000422. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202000422, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

